The mechanisms behind rising antifungal drug resistance Nature antifungal resistance antifungalresistance mechanisms resistance drugresistance
By Neha MathurJul 19 2023Reviewed by Sophia Coveney In a recent study published in npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, researchers addressed the issue of the rise of antifungal drugs-resistant infections and the advent of multidrug-resistant fungal pathogens. In addition, they described the strategies used by fungal pathogens to evolve resistance and the mechanism governing the same.
Only three classes of drugs - polyenes, azoles, and echinocandins - are currently available to combat these lethal fungal pathogens. Amphotericin B, a polyene drug, is the treatment of choice for infections caused by C. neoformans. It exhibits broad-spectrum activity against many yeast and mold species but induces host toxicity too, which disfavors its wide clinical use.
Modes of acquiring antifungal drug resistance Drug target alteration Published literature describes over 140 unique sterol 14-demethylase amino acid substitutions in C. albicans, a structural analysis of which found that while some substitutions directly affected azole binding, those occurring on the proximal surface indirectly contributed to azole resistance. Some ERG11 mutations also occurred in azole-resistant clinical isolates of C. neoformans.
Related StoriesNote that resistance to echinocandin frequently involves mutations in genes encoding the drug target, FKS1 and FKS2. These genes help in the synthesis of β-1,3-glucan, a core component of the fungal cell wall during vegetative growth and sporulation, respectively. Genomic plasticity Fungal pathogens have remarkable genomic plasticity; accordingly, they alter their genomes rapidly via aneuploidy, loss of heterozygosity events, and copy number variations , which amplify large genomic regions. In addition, heteroresistance gave rise to highly azole-resistant fungal populations. A recent study also demonstrated horizontal gene transfer -mediated antifungal resistance in A. fumigatus.
Against echinocandins, C. albicans and A. fumigatus upregulate chitin, an essential fungal cell wall polysaccharide, which helps compensate for cellular stress induced by the inhibition of glucan synthase. Drug-induced or genetic inhibition of lysine deacetylases hampers the physical interaction between Hsp90 and calcineurin proteins needed to mount cellular stress responses, often resulting in azole resistance. In addition, lysine acetyltransferases, such as Gcn5, mediate resistance in Candida species.
Danmark Seneste Nyt, Danmark Overskrifter
Similar News:Du kan også læse nyheder, der ligner denne, som vi har indsamlet fra andre nyhedskilder.
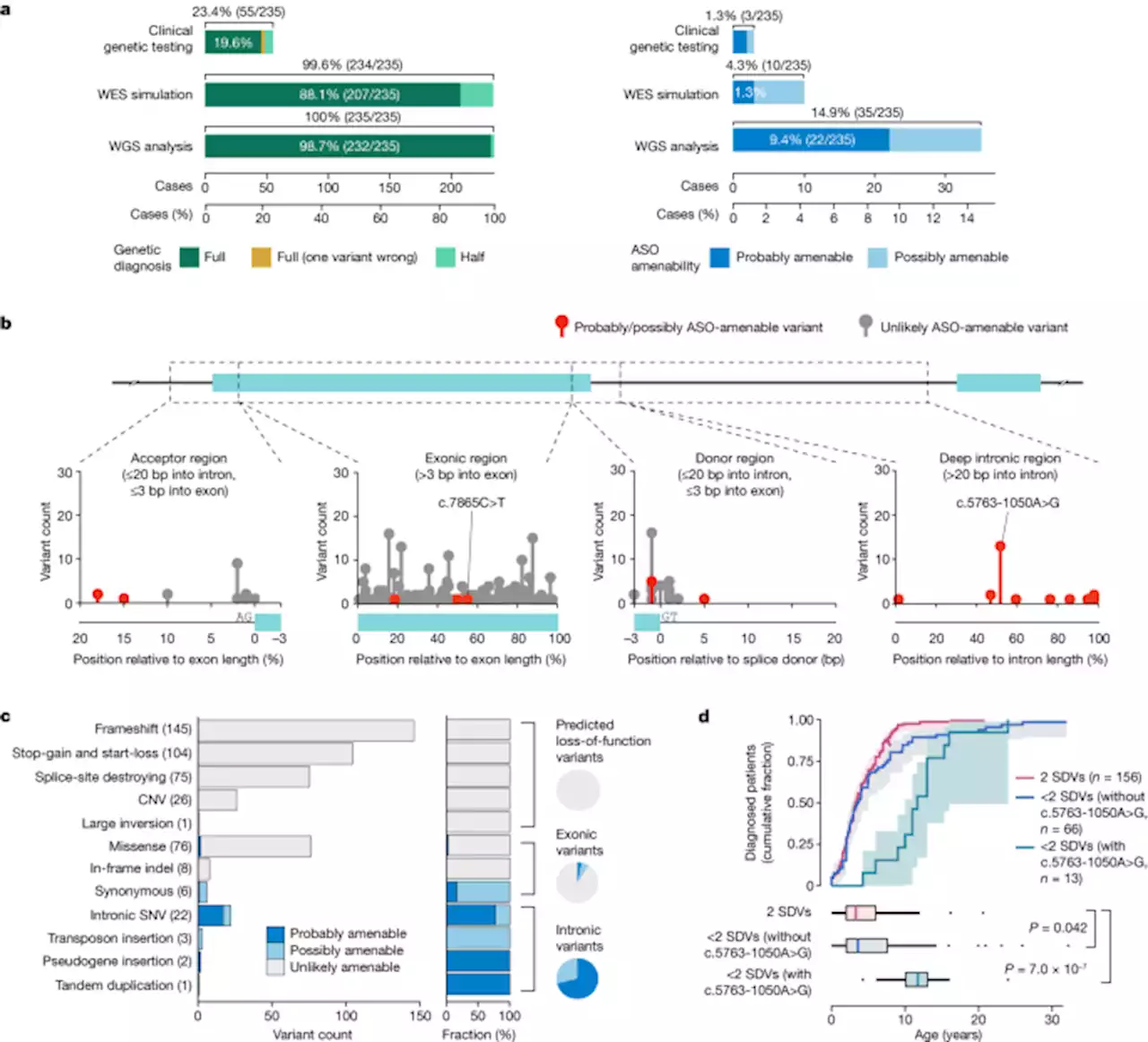 A framework for individualized splice-switching oligonucleotide therapy - NatureWhole-genome sequencing analyses in a cohort of individuals with ataxia-telangiectasia are used to identify genetic variants that might be amenable to treatment with splice-switching antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), and develop ASOs with therapeutic potential.
A framework for individualized splice-switching oligonucleotide therapy - NatureWhole-genome sequencing analyses in a cohort of individuals with ataxia-telangiectasia are used to identify genetic variants that might be amenable to treatment with splice-switching antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), and develop ASOs with therapeutic potential.
Læs mere »
 Barra Best talks extreme weather, nature and how we are 'all in this together'“I don’t remember in 13 years [doing the weather] having to report on thunderstorm warnings so much [as] this year. I think it was something 15 warnings issued between the end of April and the middle of June - I’ve never done that.'
Barra Best talks extreme weather, nature and how we are 'all in this together'“I don’t remember in 13 years [doing the weather] having to report on thunderstorm warnings so much [as] this year. I think it was something 15 warnings issued between the end of April and the middle of June - I’ve never done that.'
Læs mere »
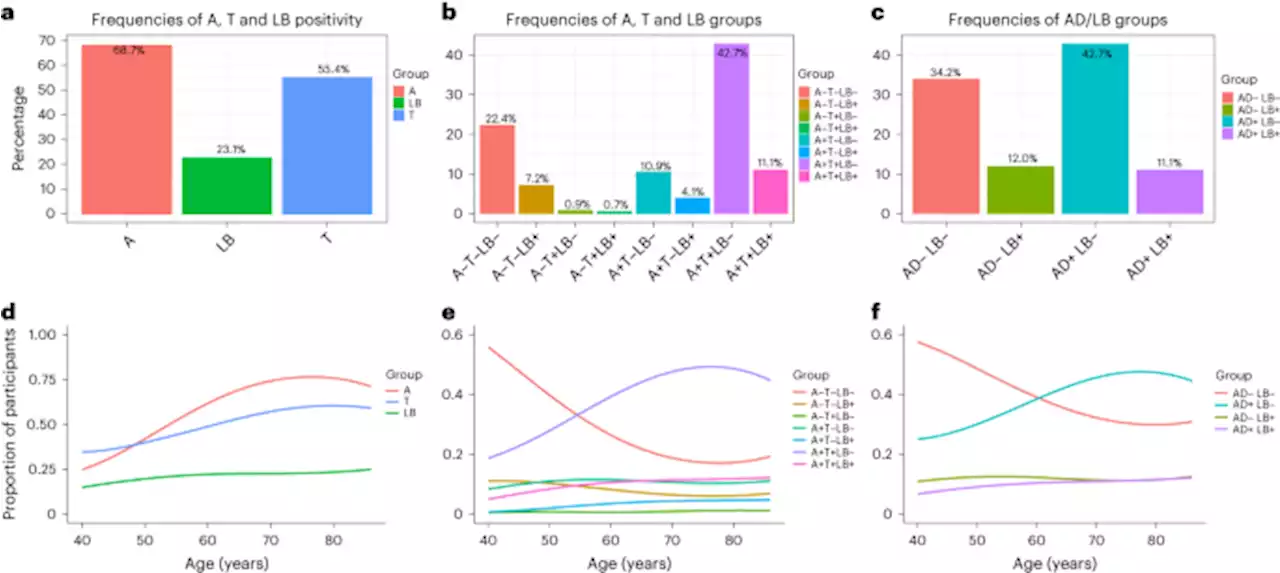 Clinical effects of Lewy body pathology in cognitively impaired individuals - Nature MedicineProspective and longitudinal analyses of patients with cognitive impairment reveal that in vivo detection of Lewy body pathology is independently associated with hallucinations, worse attention/executive, visuospatial and motor function and predicted future cognitive decline.
Clinical effects of Lewy body pathology in cognitively impaired individuals - Nature MedicineProspective and longitudinal analyses of patients with cognitive impairment reveal that in vivo detection of Lewy body pathology is independently associated with hallucinations, worse attention/executive, visuospatial and motor function and predicted future cognitive decline.
Læs mere »
 Genomic epidemiology of Vibrio cholerae during a mass vaccination campaign of displaced communities in Bangladesh - Nature CommunicationsThe Cox’s Bazar area of Bangladesh has received a large number of Forcibly Displaced Myanmar Nationals. Cholera outbreaks have been detected in the area, and here, the authors perform genomic surveillance of cholera in the refugee and non-refugee population to infer the risk of epidemic spread.
Genomic epidemiology of Vibrio cholerae during a mass vaccination campaign of displaced communities in Bangladesh - Nature CommunicationsThe Cox’s Bazar area of Bangladesh has received a large number of Forcibly Displaced Myanmar Nationals. Cholera outbreaks have been detected in the area, and here, the authors perform genomic surveillance of cholera in the refugee and non-refugee population to infer the risk of epidemic spread.
Læs mere »
 ‘The longer we take, the more people will die’ - missed promises leave Britain suffering more from heatwaves and fires, nature chief says‘The longer we take, the more people will die’ - Britain suffering more from heatwaves and fires, nature chief says
‘The longer we take, the more people will die’ - missed promises leave Britain suffering more from heatwaves and fires, nature chief says‘The longer we take, the more people will die’ - Britain suffering more from heatwaves and fires, nature chief says
Læs mere »
 Reed: Raiders not extending Josh Jacobs makes sense, but it won't make things easyPutting emotion aside is the nature of the business in the NFL, but even the most rational decision can have consequences. Josh Jacobs did everything that could be asked of a player both on and off the field. tashanreed on where the Raiders stand now.
Reed: Raiders not extending Josh Jacobs makes sense, but it won't make things easyPutting emotion aside is the nature of the business in the NFL, but even the most rational decision can have consequences. Josh Jacobs did everything that could be asked of a player both on and off the field. tashanreed on where the Raiders stand now.
Læs mere »
