Study shows low risk of myocarditis/pericarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination Coronavirus Disease COVID mRNA Myocarditis Pericarditis medrxivpreprint q_nationaltaiwa
By Dr. Sanchari Sinha Dutta, Ph.D.Oct 19 2022Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. In a recent study published on the medRxiv* preprint server, Taiwanese scientists determined the risk of myocarditis and pericarditis among young individuals who have received messenger ribonucleic acid -based coronavirus disease 2019 vaccines.
Regarding safety issues related to COVID-19 vaccines, many studies have suggested that mRNA-based vaccines might increase the risk of myocarditis and pericarditis among young individuals, particularly after the second dose. However, a high level of discrepancies has been observed between studies, which could be due to variations in ethnicities, monitoring methods, case definitions, and post-vaccination observation periods.
Prevalence of myocarditis and pericarditis The study estimated the prevalence of myocarditis and pericarditis between March 2021 and February 2022. A total of 5,957 and 2,408 adverse events had been reported following the first and second vaccination, respectively, to an online vaccine-related adversity reporting system in Taiwan.
Most patients who developed myocarditis and pericarditis after the second dose received two doses of the same vaccine at an interval of more than 90 days. Considering both genders and all age groups, the highest prevalence of myocarditis/pericarditis was observed after the second dose in males between the ages of 12-17 years for the Pfizer vaccine and males aged 18–24 years for the Moderna vaccine.
Danmark Seneste Nyt, Danmark Overskrifter
Similar News:Du kan også læse nyheder, der ligner denne, som vi har indsamlet fra andre nyhedskilder.
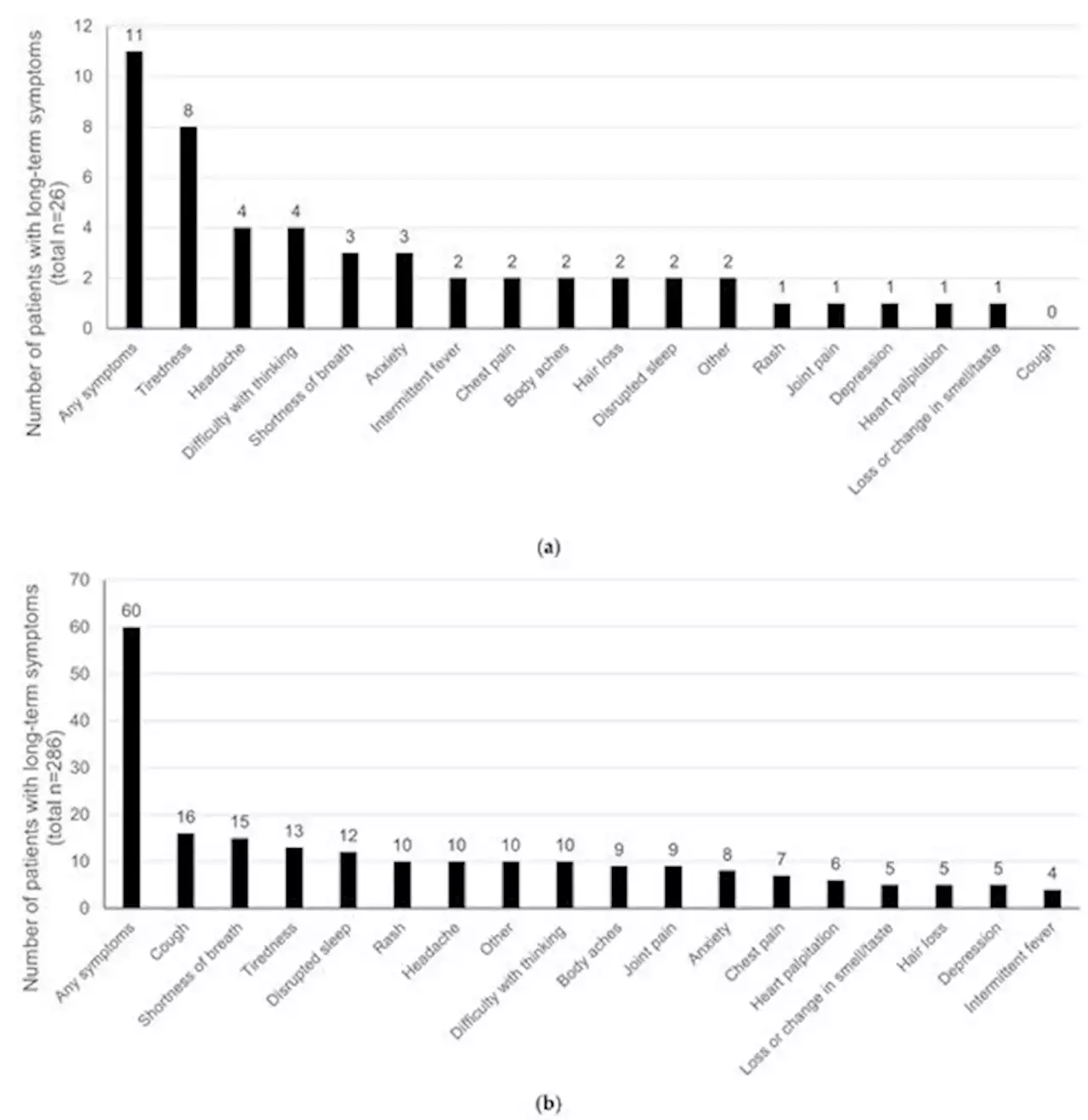 Comparison of Long-Term Complications of COVID-19 Illness among a Diverse Sample of Children by MIS-C StatusMost pediatric COVID-19 cases are asymptomatic; however, a small number of children are diagnosed with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), a rare but severe condition that is associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Persistent symptoms of COVID-19 illness in children diagnosed with/without MIS-C is largely unknown. A retrospective EHR review of patients with COVID-19 illness from one pediatric healthcare system to assess the presence of acute (<30 days) and chronic (≥30, 60–120, and >120 days) long-term COVID symptoms was conducted. Patients/caregivers completed a follow-up survey from March 2021 to January 2022 to assess the presence of long COVID. Results showed that non-MIS-C children (n=286; 54.49% Hispanic; 19.23% non-Hispanic Black; 5.77% other ethnicity; 79.49% government insurance) were younger (mean age 6.43 years [SD 5.95]) versus MIS-C (n=26) children (mean age 9.08 years, [SD 4.86]) (p=0.032). A share of 11.5% of children with MIS-C and 37.8% without MIS-C reported acute long COVID while 26.9% and 15.3% reported chronic long COVID, respectively. Females were almost twice as likely to report long symptoms versus males and those with private insurance were 66% less likely to report long symptoms versus those with government insurance. In conclusion, a substantial proportion of ethnically diverse children from low resource backgrounds with severe COVID illness are reporting long-term impacts. Findings can inform pediatric professionals about this vulnerable population in post-COVID-19 recovery efforts.
Comparison of Long-Term Complications of COVID-19 Illness among a Diverse Sample of Children by MIS-C StatusMost pediatric COVID-19 cases are asymptomatic; however, a small number of children are diagnosed with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), a rare but severe condition that is associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Persistent symptoms of COVID-19 illness in children diagnosed with/without MIS-C is largely unknown. A retrospective EHR review of patients with COVID-19 illness from one pediatric healthcare system to assess the presence of acute (<30 days) and chronic (≥30, 60–120, and >120 days) long-term COVID symptoms was conducted. Patients/caregivers completed a follow-up survey from March 2021 to January 2022 to assess the presence of long COVID. Results showed that non-MIS-C children (n=286; 54.49% Hispanic; 19.23% non-Hispanic Black; 5.77% other ethnicity; 79.49% government insurance) were younger (mean age 6.43 years [SD 5.95]) versus MIS-C (n=26) children (mean age 9.08 years, [SD 4.86]) (p=0.032). A share of 11.5% of children with MIS-C and 37.8% without MIS-C reported acute long COVID while 26.9% and 15.3% reported chronic long COVID, respectively. Females were almost twice as likely to report long symptoms versus males and those with private insurance were 66% less likely to report long symptoms versus those with government insurance. In conclusion, a substantial proportion of ethnically diverse children from low resource backgrounds with severe COVID illness are reporting long-term impacts. Findings can inform pediatric professionals about this vulnerable population in post-COVID-19 recovery efforts.
Læs mere »
 Cancer vaccine could become available by 2030, scientists behind COVID jab sayThe BioNTech founders, responsible for the lifesaving Covid vaccine, are now back with new discoveries to destroy cancer cells.
Cancer vaccine could become available by 2030, scientists behind COVID jab sayThe BioNTech founders, responsible for the lifesaving Covid vaccine, are now back with new discoveries to destroy cancer cells.
Læs mere »
 Risk of thyroid dysfunction associated with mRNA and inactivated COVID-19 vaccines: a population-based study of 2.3 million vaccine recipients - BMC MedicineBackground In view of accumulating case reports of thyroid dysfunction following COVID-19 vaccination, we evaluated the risks of incident thyroid dysfunction following inactivated (CoronaVac) and mRNA (BNT162b2) COVID-19 vaccines using a population-based dataset. Methods We identified people who received COVID-19 vaccination between 23 February and 30 September 2021 from a population-based electronic health database in Hong Kong, linked to vaccination records. Thyroid dysfunction encompassed anti-thyroid drug (ATD)/levothyroxine (LT4) initiation, biochemical picture of hyperthyroidism/hypothyroidism, incident Graves’ disease (GD), and thyroiditis. A self-controlled case series design was used to estimate the incidence rate ratio (IRR) of thyroid dysfunction in a 56-day post-vaccination period compared to the baseline period (non-exposure period) using conditional Poisson regression. Results A total of 2,288,239 people received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccination (57.8% BNT162b2 recipients and 42.2% CoronaVac recipients). 94.3% of BNT162b2 recipients and 92.2% of CoronaVac recipients received the second dose. Following the first dose of COVID-19 vaccination, there was no increase in the risks of ATD initiation (BNT162b2: IRR 0.864, 95% CI 0.670–1.114; CoronaVac: IRR 0.707, 95% CI 0.549–0.912), LT4 initiation (BNT162b2: IRR 0.911, 95% CI 0.716–1.159; CoronaVac: IRR 0.778, 95% CI 0.618–0.981), biochemical picture of hyperthyroidism (BNT162b2: IRR 0.872, 95% CI 0.744–1.023; CoronaVac: IRR 0.830, 95% CI 0.713–0.967) or hypothyroidism (BNT162b2: IRR 1.002, 95% CI 0.838–1.199; CoronaVac: IRR 0.963, 95% CI 0.807–1.149), GD, and thyroiditis. Similarly, following the second dose of COVID-19 vaccination, there was no increase in the risks of ATD initiation (BNT162b2: IRR 0.972, 95% CI 0.770–1.227; CoronaVac: IRR 0.879, 95%CI 0.693–1.116), LT4 initiation (BNT162b2: IRR 1.019, 95% CI 0.833–1.246; CoronaVac: IRR 0.768, 95% CI 0.613–0.962), hyperthyroidism (BNT162b2: IRR 1.0
Risk of thyroid dysfunction associated with mRNA and inactivated COVID-19 vaccines: a population-based study of 2.3 million vaccine recipients - BMC MedicineBackground In view of accumulating case reports of thyroid dysfunction following COVID-19 vaccination, we evaluated the risks of incident thyroid dysfunction following inactivated (CoronaVac) and mRNA (BNT162b2) COVID-19 vaccines using a population-based dataset. Methods We identified people who received COVID-19 vaccination between 23 February and 30 September 2021 from a population-based electronic health database in Hong Kong, linked to vaccination records. Thyroid dysfunction encompassed anti-thyroid drug (ATD)/levothyroxine (LT4) initiation, biochemical picture of hyperthyroidism/hypothyroidism, incident Graves’ disease (GD), and thyroiditis. A self-controlled case series design was used to estimate the incidence rate ratio (IRR) of thyroid dysfunction in a 56-day post-vaccination period compared to the baseline period (non-exposure period) using conditional Poisson regression. Results A total of 2,288,239 people received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccination (57.8% BNT162b2 recipients and 42.2% CoronaVac recipients). 94.3% of BNT162b2 recipients and 92.2% of CoronaVac recipients received the second dose. Following the first dose of COVID-19 vaccination, there was no increase in the risks of ATD initiation (BNT162b2: IRR 0.864, 95% CI 0.670–1.114; CoronaVac: IRR 0.707, 95% CI 0.549–0.912), LT4 initiation (BNT162b2: IRR 0.911, 95% CI 0.716–1.159; CoronaVac: IRR 0.778, 95% CI 0.618–0.981), biochemical picture of hyperthyroidism (BNT162b2: IRR 0.872, 95% CI 0.744–1.023; CoronaVac: IRR 0.830, 95% CI 0.713–0.967) or hypothyroidism (BNT162b2: IRR 1.002, 95% CI 0.838–1.199; CoronaVac: IRR 0.963, 95% CI 0.807–1.149), GD, and thyroiditis. Similarly, following the second dose of COVID-19 vaccination, there was no increase in the risks of ATD initiation (BNT162b2: IRR 0.972, 95% CI 0.770–1.227; CoronaVac: IRR 0.879, 95%CI 0.693–1.116), LT4 initiation (BNT162b2: IRR 1.019, 95% CI 0.833–1.246; CoronaVac: IRR 0.768, 95% CI 0.613–0.962), hyperthyroidism (BNT162b2: IRR 1.0
Læs mere »
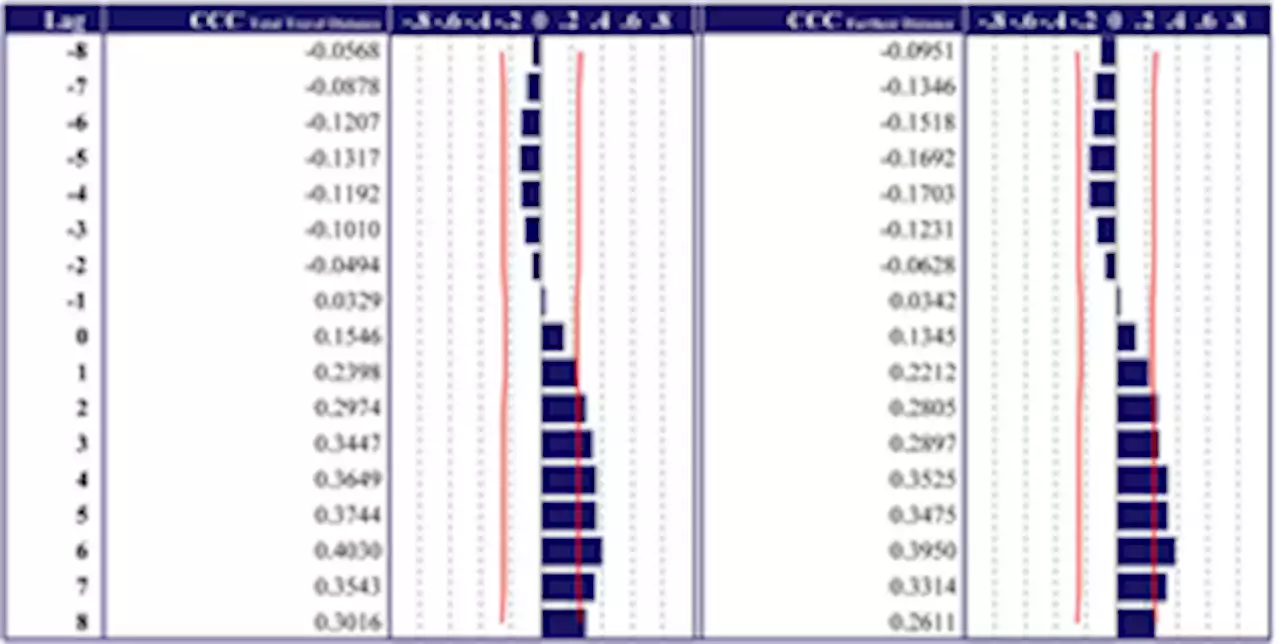 Time series cross-correlation between home range and number of infected people during the COVID-19 pandemic in a suburban cityControl of human mobility is one of the most effective measures to prevent the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, the imposition of emergency restrictions had significant negative impacts on citizens’ daily lives. As vaccination progresses, we need to consider more effective measures to control the spread of the infection. The research question of this study is as follows: Does the control of home range correlate with a reduction in the number of infected people during the COVID-19 pandemic? This study aims to clarify the correlation between home range and the number of people infected with SARS-CoV-2 during the COVID-19 pandemic in Ibaraki City. Home ranges are analyzed by the Minimum Convex Polygon method using mobile phone GPS location history data. We analyzed the time series cross-correlation between home range lengths and the number of infected people. Results reveal a slight positive correlation between home range and the number of infected people after one week during the COVID-19 pandemic. Regarding home range length, the cross-correlation coefficient is 0.4030 even at a lag level of six weeks, which has the most significant coefficient. Thus, a decrease in the home range is a weak factor correlated with a reduction in the number of infected people. This study makes a significant contribution to the literature by evaluating key public health challenges from the perspective of controliing the spread of the COVID-19 infectuion. Its findings has implications for policy makers, practitioners, and urban scientists seeking to promote urban sustainability.
Time series cross-correlation between home range and number of infected people during the COVID-19 pandemic in a suburban cityControl of human mobility is one of the most effective measures to prevent the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, the imposition of emergency restrictions had significant negative impacts on citizens’ daily lives. As vaccination progresses, we need to consider more effective measures to control the spread of the infection. The research question of this study is as follows: Does the control of home range correlate with a reduction in the number of infected people during the COVID-19 pandemic? This study aims to clarify the correlation between home range and the number of people infected with SARS-CoV-2 during the COVID-19 pandemic in Ibaraki City. Home ranges are analyzed by the Minimum Convex Polygon method using mobile phone GPS location history data. We analyzed the time series cross-correlation between home range lengths and the number of infected people. Results reveal a slight positive correlation between home range and the number of infected people after one week during the COVID-19 pandemic. Regarding home range length, the cross-correlation coefficient is 0.4030 even at a lag level of six weeks, which has the most significant coefficient. Thus, a decrease in the home range is a weak factor correlated with a reduction in the number of infected people. This study makes a significant contribution to the literature by evaluating key public health challenges from the perspective of controliing the spread of the COVID-19 infectuion. Its findings has implications for policy makers, practitioners, and urban scientists seeking to promote urban sustainability.
Læs mere »
 Covid 'very much still out there' as people urged to get boosterStaff at Nottingham's vaccine hub are advising more people to come down
Covid 'very much still out there' as people urged to get boosterStaff at Nottingham's vaccine hub are advising more people to come down
Læs mere »
 Glastonbury 2023: 'Challenging times' blamed for ticket price riseEmily Eavis says the festival is 'still recovering' from the financial cost of Covid.
Glastonbury 2023: 'Challenging times' blamed for ticket price riseEmily Eavis says the festival is 'still recovering' from the financial cost of Covid.
Læs mere »
