A study published in BMCMedicine finds no evidence of a vaccine-related increase in incident hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism with both the Pfizer BioNTech and Sinovac-CoronaVac COVID-19 vaccines.
]. The modified SCCS requires including unvaccinated people during the observation period to inform the timing of the events by adjusting for the monthly seasonal effects.
Subgroup analyses were conducted by age among men and women separately due to different sex distributions between the younger and older.
Regarding hypothyroid-related outcomes, the incidences of biochemical hypothyroidism and LT4 initiation were 26.5 and 21.3 cases per 100,000 doses following the first dose of BNT162b2, 46.9 and 48.2 cases per 100,000 doses following the second dose of BNT162b2, 36.8 and 33.2 cases per 100,000 doses following the first dose of CoronaVac, and 52.0 and 49.5 cases per 100,000 doses following the second dose of CoronaVac.summarises the outcomes of thyroid dysfunction among the vaccine recipients.
Table 1 Risks of thyroid dysfunction in the 56-day risk period following the first or second dose of COVID-19 vaccinationThe IRRs for hypothyroid-related outcomes of interest compared to the baseline period indicated no significant increase in the risk of biochemical hypothyroidism , initiation of LT4 related to the first doses of COVID-19 vaccine.
The results of the subgroup and sensitivity analyses were consistent with the main analysis . There was no change in the results when the risk period was shortened to as early as 3 weeks post-vaccination.This is the first population-based study of the risk of incident thyroid dysfunction associated with COVID-19 vaccination.
Danmark Seneste Nyt, Danmark Overskrifter
Similar News:Du kan også læse nyheder, der ligner denne, som vi har indsamlet fra andre nyhedskilder.
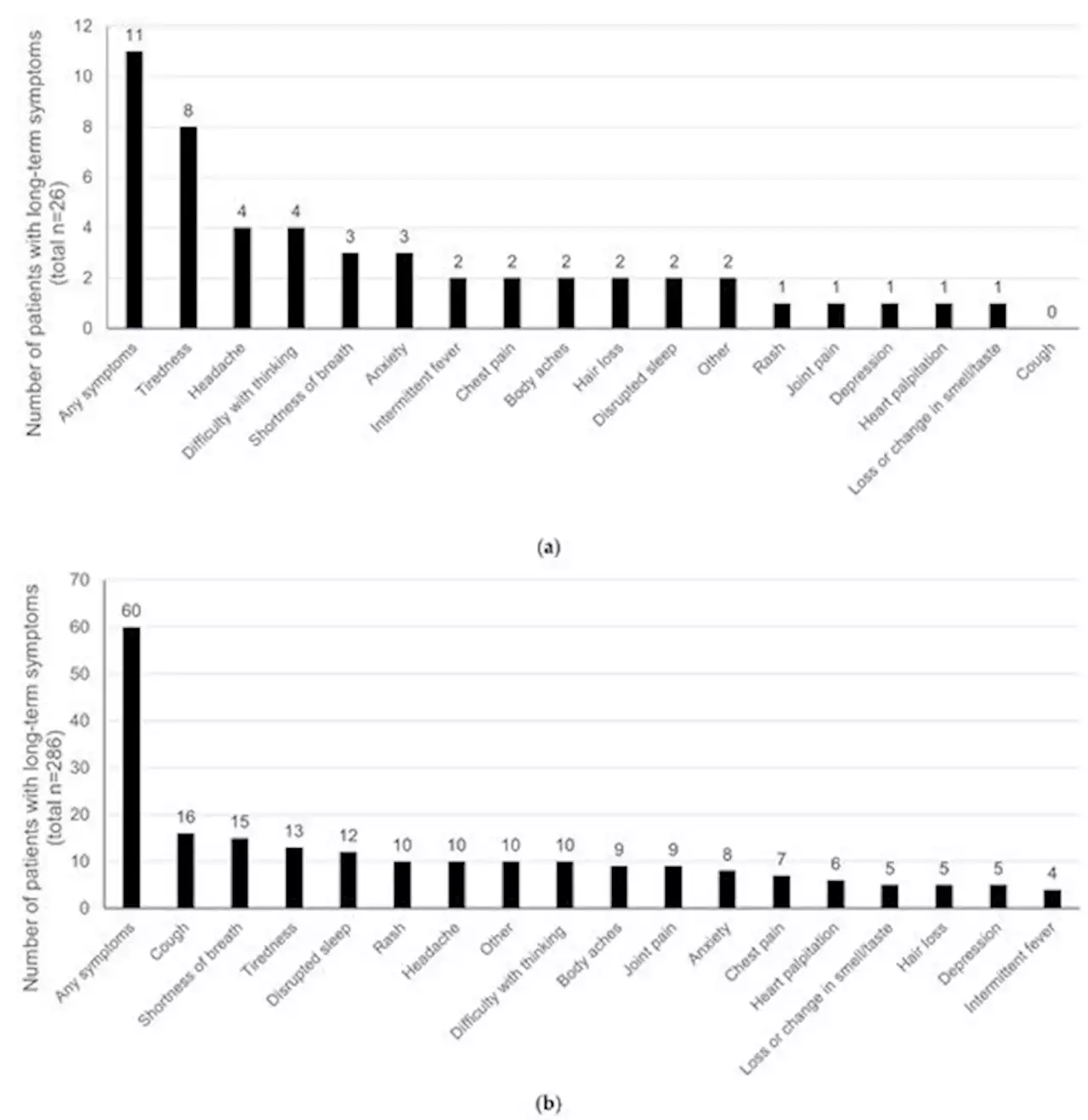 Comparison of Long-Term Complications of COVID-19 Illness among a Diverse Sample of Children by MIS-C StatusMost pediatric COVID-19 cases are asymptomatic; however, a small number of children are diagnosed with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), a rare but severe condition that is associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Persistent symptoms of COVID-19 illness in children diagnosed with/without MIS-C is largely unknown. A retrospective EHR review of patients with COVID-19 illness from one pediatric healthcare system to assess the presence of acute (<30 days) and chronic (≥30, 60–120, and >120 days) long-term COVID symptoms was conducted. Patients/caregivers completed a follow-up survey from March 2021 to January 2022 to assess the presence of long COVID. Results showed that non-MIS-C children (n=286; 54.49% Hispanic; 19.23% non-Hispanic Black; 5.77% other ethnicity; 79.49% government insurance) were younger (mean age 6.43 years [SD 5.95]) versus MIS-C (n=26) children (mean age 9.08 years, [SD 4.86]) (p=0.032). A share of 11.5% of children with MIS-C and 37.8% without MIS-C reported acute long COVID while 26.9% and 15.3% reported chronic long COVID, respectively. Females were almost twice as likely to report long symptoms versus males and those with private insurance were 66% less likely to report long symptoms versus those with government insurance. In conclusion, a substantial proportion of ethnically diverse children from low resource backgrounds with severe COVID illness are reporting long-term impacts. Findings can inform pediatric professionals about this vulnerable population in post-COVID-19 recovery efforts.
Comparison of Long-Term Complications of COVID-19 Illness among a Diverse Sample of Children by MIS-C StatusMost pediatric COVID-19 cases are asymptomatic; however, a small number of children are diagnosed with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), a rare but severe condition that is associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Persistent symptoms of COVID-19 illness in children diagnosed with/without MIS-C is largely unknown. A retrospective EHR review of patients with COVID-19 illness from one pediatric healthcare system to assess the presence of acute (<30 days) and chronic (≥30, 60–120, and >120 days) long-term COVID symptoms was conducted. Patients/caregivers completed a follow-up survey from March 2021 to January 2022 to assess the presence of long COVID. Results showed that non-MIS-C children (n=286; 54.49% Hispanic; 19.23% non-Hispanic Black; 5.77% other ethnicity; 79.49% government insurance) were younger (mean age 6.43 years [SD 5.95]) versus MIS-C (n=26) children (mean age 9.08 years, [SD 4.86]) (p=0.032). A share of 11.5% of children with MIS-C and 37.8% without MIS-C reported acute long COVID while 26.9% and 15.3% reported chronic long COVID, respectively. Females were almost twice as likely to report long symptoms versus males and those with private insurance were 66% less likely to report long symptoms versus those with government insurance. In conclusion, a substantial proportion of ethnically diverse children from low resource backgrounds with severe COVID illness are reporting long-term impacts. Findings can inform pediatric professionals about this vulnerable population in post-COVID-19 recovery efforts.
Læs mere »
 Pathophysiology of Post-COVID syndromes: a new perspective - Virology JournalMost COVID-19 patients recovered with low mortality; however, some patients experienced long-term symptoms described as “long-COVID” or “Post-COVID syndrome” (PCS). Patients may have persisting symptoms for weeks after acute SARS-CoV-2 infection, including dyspnea, fatigue, myalgia, insomnia, cognitive and olfactory disorders. These symptoms may last for months in some patients. PCS may progress in association with the development of mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS), which is a distinct kind of mast cell activation disorder, characterized by hyper-activation of mast cells with inappropriate and excessive release of chemical mediators. COVID-19 survivors, mainly women, and patients with persistent severe fatigue for 10 weeks after recovery with a history of neuropsychiatric disorders are more prone to develop PCS. High D-dimer levels and blood urea nitrogen were observed to be risk factors associated with pulmonary dysfunction in COVID-19 survivors 3 months post-hospital discharge with the development of PCS. PCS has systemic manifestations that resolve with time with no further complications. However, the final outcomes of PCS are chiefly unknown. Persistence of inflammatory reactions, autoimmune mimicry, and reactivation of pathogens together with host microbiome alterations may contribute to the development of PCS. The deregulated release of inflammatory mediators in MCAS produces extraordinary symptoms in patients with PCS. The development of MCAS during the course of SARS-CoV-2 infection is correlated to COVID-19 severity and the development of PCS. Therefore, MCAS is treated by antihistamines, inhibition of synthesis of mediators, inhibition of mediator release, and inhibition of degranulation of mast cells.
Pathophysiology of Post-COVID syndromes: a new perspective - Virology JournalMost COVID-19 patients recovered with low mortality; however, some patients experienced long-term symptoms described as “long-COVID” or “Post-COVID syndrome” (PCS). Patients may have persisting symptoms for weeks after acute SARS-CoV-2 infection, including dyspnea, fatigue, myalgia, insomnia, cognitive and olfactory disorders. These symptoms may last for months in some patients. PCS may progress in association with the development of mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS), which is a distinct kind of mast cell activation disorder, characterized by hyper-activation of mast cells with inappropriate and excessive release of chemical mediators. COVID-19 survivors, mainly women, and patients with persistent severe fatigue for 10 weeks after recovery with a history of neuropsychiatric disorders are more prone to develop PCS. High D-dimer levels and blood urea nitrogen were observed to be risk factors associated with pulmonary dysfunction in COVID-19 survivors 3 months post-hospital discharge with the development of PCS. PCS has systemic manifestations that resolve with time with no further complications. However, the final outcomes of PCS are chiefly unknown. Persistence of inflammatory reactions, autoimmune mimicry, and reactivation of pathogens together with host microbiome alterations may contribute to the development of PCS. The deregulated release of inflammatory mediators in MCAS produces extraordinary symptoms in patients with PCS. The development of MCAS during the course of SARS-CoV-2 infection is correlated to COVID-19 severity and the development of PCS. Therefore, MCAS is treated by antihistamines, inhibition of synthesis of mediators, inhibition of mediator release, and inhibition of degranulation of mast cells.
Læs mere »
 Do phthalates in face masks pose health hazards with increased usage during the COVID-19 pandemic?In a new study, researchers investigated the presence of phthalic acid esters (PAEs) or phthalates in commercially available face masks to assess the health risks associated with the increased use of face masks during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
Do phthalates in face masks pose health hazards with increased usage during the COVID-19 pandemic?In a new study, researchers investigated the presence of phthalic acid esters (PAEs) or phthalates in commercially available face masks to assess the health risks associated with the increased use of face masks during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
Læs mere »
 Can adherence to COVID-19 mitigation measures be predicted using cognitive variables?In a new study, researchers investigated the correlations between cognitive variables such as self-control, impulsivity, and future orientation and disease mitigation behaviors associated with the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
Can adherence to COVID-19 mitigation measures be predicted using cognitive variables?In a new study, researchers investigated the correlations between cognitive variables such as self-control, impulsivity, and future orientation and disease mitigation behaviors associated with the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
Læs mere »
 WWE boss Triple H tests positive for Covid-19 and will miss tonight's RawBREAKING: WWE boss Triple H has reportedly tested positive for Covid-19 and will miss tonight’s episode of Raw.
WWE boss Triple H tests positive for Covid-19 and will miss tonight's RawBREAKING: WWE boss Triple H has reportedly tested positive for Covid-19 and will miss tonight’s episode of Raw.
Læs mere »