Comparing post–COVID-19 symptoms two years after SARS-CoV-2 infection URJCcientifica COVID19 SARSCoV2 Coronavirus PostCOVID Symptoms
By Neha MathurNov 17 2022Reviewed by Aimee Molineux In a recent study published in JAMA Network Open, researchers compared the presence of post–coronavirus disease 2019 symptoms among hospitalized and nonhospitalized patients in Spain.
Studies have reported over 100 post–COVID-19 symptoms affecting multiple human organs . Several reviews have evidenced that people experiencing post–COVID-19 symptoms have worsened health-related quality of life. About the study In the present study, researchers recruited patients hospitalized with COVID-19 from two urban hospitals in Spain and another group of hospitalized patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 from an outpatient setting managed by their general practitioners. They used Microsoft randomization software to select 400 patients for each study group. The current cross-sectional study followed the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology reporting guidelines.
Related StoriesThe researchers pursued evidence of the emotional and societal impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. So they used the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale and the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index for anxiety & depressive symptoms, and sleep quality assessments, respectively. For the HADS-A and HADS-D, a cutoff score of 12 or 10 points or more indicated anxiety and depressive symptoms, respectively.
The researchers noted that dyspnea and anosmia were the most prevalent COVID-19–associated symptoms at onset among hospitalized and nonhospitalized patients, respectively. While the former is an annoying symptom experienced during severe illness, the latter delineates COVID-19 from clinical manifestations of other respiratory infections. Also, people experiencing anosmia often did not seek hospital admission.
Danmark Seneste Nyt, Danmark Overskrifter
Similar News:Du kan også læse nyheder, der ligner denne, som vi har indsamlet fra andre nyhedskilder.
 Researchers identify a conserved site on SARS-CoV-2 spike that a broadly neutralizing macrocyclic peptide can targetResearchers identify a conserved site on SARS-CoV-2 spike that a broadly neutralizing macrocyclic peptide can target biorxivpreprint UniUtrecht ANUmedia Sydney_Uni SARSCoV2 spike coronavirus covid COVID19 peptide
Researchers identify a conserved site on SARS-CoV-2 spike that a broadly neutralizing macrocyclic peptide can targetResearchers identify a conserved site on SARS-CoV-2 spike that a broadly neutralizing macrocyclic peptide can target biorxivpreprint UniUtrecht ANUmedia Sydney_Uni SARSCoV2 spike coronavirus covid COVID19 peptide
Læs mere »
 SARS-CoV-2 open reading frame 3c protein found to be targeted selectively to mitochondriaSARS-CoV-2 open reading frame 3c protein found to be targeted selectively to mitochondria biorxivpreprint Cambridge_Uni helsinkiuni SARSCoV2 COVID19 Mitochondria
SARS-CoV-2 open reading frame 3c protein found to be targeted selectively to mitochondriaSARS-CoV-2 open reading frame 3c protein found to be targeted selectively to mitochondria biorxivpreprint Cambridge_Uni helsinkiuni SARSCoV2 COVID19 Mitochondria
Læs mere »
 SARS-CoV-2 ‘Deltacron’ variant exhibits immune-escape properties similar to Omicron BA.1SARS-CoV-2 ‘Deltacron’ variant exhibits immune-escape properties similar to Omicron BA.1 Omicron Coronavirus Disease COVID IJMS_MDPI leibnizprimate uniGoettingen HannoverMh
SARS-CoV-2 ‘Deltacron’ variant exhibits immune-escape properties similar to Omicron BA.1SARS-CoV-2 ‘Deltacron’ variant exhibits immune-escape properties similar to Omicron BA.1 Omicron Coronavirus Disease COVID IJMS_MDPI leibnizprimate uniGoettingen HannoverMh
Læs mere »
 SARS-CoV-2 antibodies persist in breast milk following two and three COVID-19 vaccine dosesSARS-CoV-2 antibodies persist in breast milk following two and three COVID-19 vaccine doses BreastMilk Coronavirus Disease COVID SARSCoV2 Vaccine SSRN TheLancet UCSF
SARS-CoV-2 antibodies persist in breast milk following two and three COVID-19 vaccine dosesSARS-CoV-2 antibodies persist in breast milk following two and three COVID-19 vaccine doses BreastMilk Coronavirus Disease COVID SARSCoV2 Vaccine SSRN TheLancet UCSF
Læs mere »
 Protection afforded by SARS-CoV-2 infection against reinfection when Omicron BA.5 was the dominating subvariant in Scania county, SwedenProtection afforded by SARS-CoV-2 infection against reinfection when Omicron BA.5 was the dominating subvariant in Scania county, Sweden medrxivpreprint lunduniversity goteborgsuni SARSCoV2 infection reinfection Omicron
Protection afforded by SARS-CoV-2 infection against reinfection when Omicron BA.5 was the dominating subvariant in Scania county, SwedenProtection afforded by SARS-CoV-2 infection against reinfection when Omicron BA.5 was the dominating subvariant in Scania county, Sweden medrxivpreprint lunduniversity goteborgsuni SARSCoV2 infection reinfection Omicron
Læs mere »
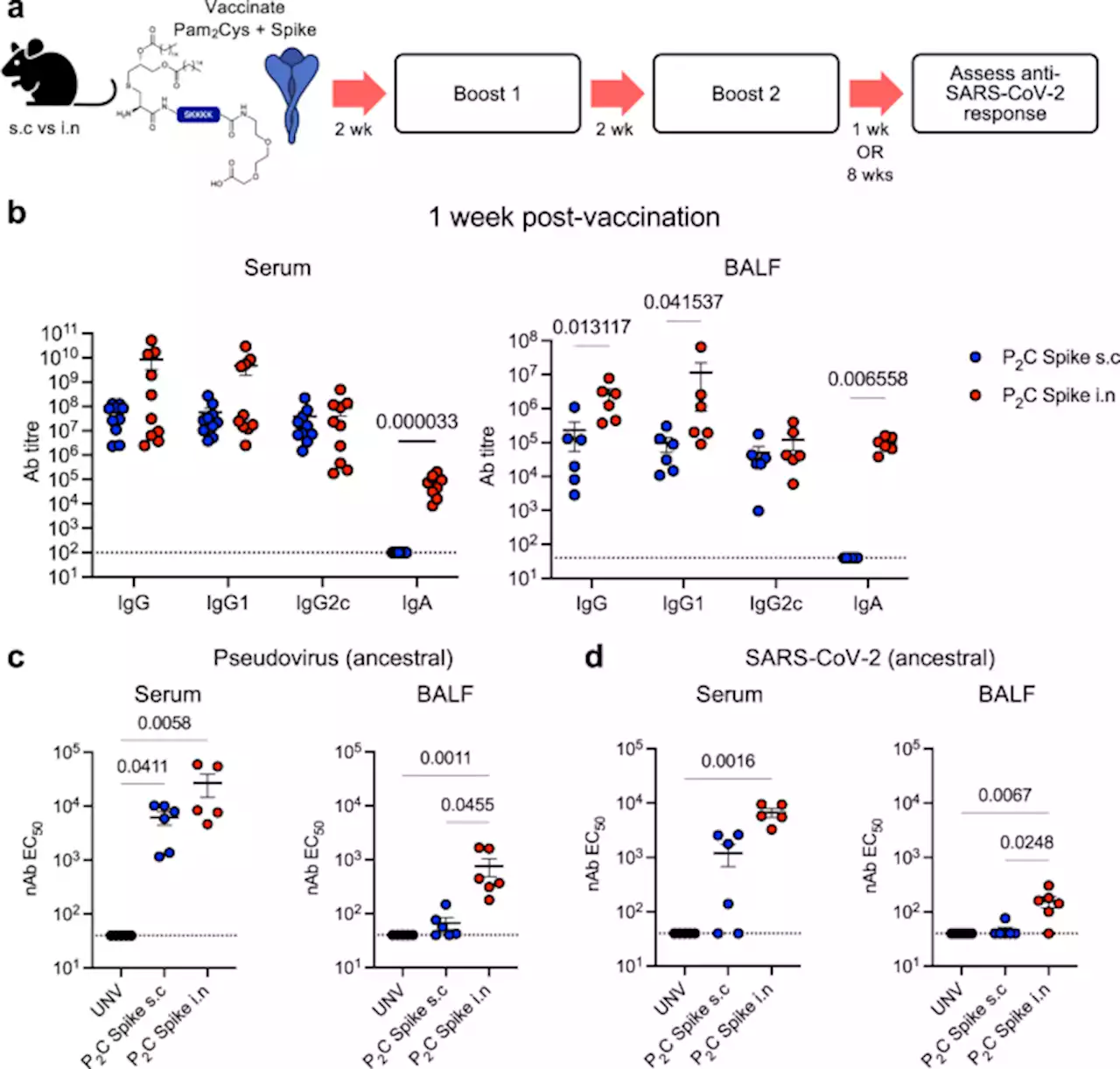 Mucosal TLR2-activating protein-based vaccination induces potent pulmonary immunity and protection against SARS-CoV-2 in mice - Nature CommunicationsCurrent vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 reduce mortality but are less effective in preventing infection. Here the authors show that intranasal vaccination with a subunit vaccine including an TLR2-stimulating adjuvant induces strong neutralising antibody and T-cell responses against SARS-CoV-2 in the lungs that protect against infection.
Mucosal TLR2-activating protein-based vaccination induces potent pulmonary immunity and protection against SARS-CoV-2 in mice - Nature CommunicationsCurrent vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 reduce mortality but are less effective in preventing infection. Here the authors show that intranasal vaccination with a subunit vaccine including an TLR2-stimulating adjuvant induces strong neutralising antibody and T-cell responses against SARS-CoV-2 in the lungs that protect against infection.
Læs mere »
