In an On Medicine blog for World Antimicrobial Awareness Week, salam_rasha and colleagues discuss the factors affecting the effective and appropriate use of antibiotics in two acute care settings, before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. WAAW2022
World Health Organisation Slogan for Antimicrobial Awareness Week 2022. Photo credit Rasha Abdelsalam ElshenawyA Possible Solution for Antimicrobial Resistance In a blog for World Antimicrobial Awareness Week, Rasha Abdelsalam Elshenawy, Dr Nikkie Umaru, and Dr Zoe Aslanpour discuss their study investigating the factors affecting the Antimicrobial Stewardship implementation in acute care settings before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The WHO World Antimicrobial Awareness Week is part of a global action plan to raise awareness and take action against the growing issue of AMR. The theme for World Antimicrobial Awareness Week in 2022 is “Preventing Antimicrobial Resistance Together”, and calls upon the general public, health workers, and policymakers to work together to use antimicrobials prudently and to take action to prevent AMR.
COVID-19 and Antimicrobial Resistance In June 2022, the global estimate for the number of deaths from COVID-19 was about 6 million, 10% of the worldwide deaths of 60 million. When COVID-19 cases were admitted to hospitals, antibiotics were frequently started. Several studies have also shown that patients with COVID-19 were rarely infected with bacteria when admitted. During the COVID-19 pandemic, many bacterial infections went potentially undiagnosed and untreated.
The Third Study: Cross-Sectional Study This study will explore the knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions of healthcare professionals, such as doctors, pharmacists, and nurses, toward antibiotic prescribing and factors affecting the AMS implementation at Bedfordshire Hospitals NHS Trust before and during the pandemic.
Danmark Seneste Nyt, Danmark Overskrifter
Similar News:Du kan også læse nyheder, der ligner denne, som vi har indsamlet fra andre nyhedskilder.
 The negative impact of COVID-19 on working memory revealed using a rapid online quizAlthough coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) affects the respiratory system, it can also have neurological consequences leading to cognitive deficits such as memory problems. The aim of our study was to assess the impact of COVID-19 on working memory function. We developed and implemented an online anonymous survey with a working memory quiz incorporating aspects of gamification to engage participants. 5428 participants successfully completed the survey and memory quiz between 8th December 2020 and 5th July 2021 (68.6% non-COVID-19 and 31.4% COVID-19). Most participants (93.3%) completed the survey and memory quiz relatively rapidly (mean time of 8.84 minutes). Categorical regression was used to assess the contribution of COVID status, age, time post-COVID (number of months elapsed since having had COVID), symptoms, ongoing symptoms and gender, followed by non-parametric statistics. A principal component analysis explored the relationship between subjective ratings and objective memory scores. The objective memory scores were significantly correlated with participants’ own assessment of their cognitive function. The factors significantly affecting memory scores were COVID status, age, time post-COVID and ongoing symptoms. Our main finding was a significant reduction in memory scores in all COVID groups (self-reported, positive-tested and hospitalized) compared to the non-COVID group. Memory scores for all COVID groups combined were significantly reduced compared to the non-COVID group in every age category 25 years and over, but not for the youngest age category (18–24 years old). We found that memory scores gradually increased over a period of 17 months post-COVID-19. However, those with ongoing COVID-19 symptoms continued to show a reduction in memory scores. Our findings demonstrate that COVID-19 negatively impacts working memory function, but only in adults aged 25 years and over. Moreover, our results suggest that working memory deficits with COVID-19 can recov
The negative impact of COVID-19 on working memory revealed using a rapid online quizAlthough coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) affects the respiratory system, it can also have neurological consequences leading to cognitive deficits such as memory problems. The aim of our study was to assess the impact of COVID-19 on working memory function. We developed and implemented an online anonymous survey with a working memory quiz incorporating aspects of gamification to engage participants. 5428 participants successfully completed the survey and memory quiz between 8th December 2020 and 5th July 2021 (68.6% non-COVID-19 and 31.4% COVID-19). Most participants (93.3%) completed the survey and memory quiz relatively rapidly (mean time of 8.84 minutes). Categorical regression was used to assess the contribution of COVID status, age, time post-COVID (number of months elapsed since having had COVID), symptoms, ongoing symptoms and gender, followed by non-parametric statistics. A principal component analysis explored the relationship between subjective ratings and objective memory scores. The objective memory scores were significantly correlated with participants’ own assessment of their cognitive function. The factors significantly affecting memory scores were COVID status, age, time post-COVID and ongoing symptoms. Our main finding was a significant reduction in memory scores in all COVID groups (self-reported, positive-tested and hospitalized) compared to the non-COVID group. Memory scores for all COVID groups combined were significantly reduced compared to the non-COVID group in every age category 25 years and over, but not for the youngest age category (18–24 years old). We found that memory scores gradually increased over a period of 17 months post-COVID-19. However, those with ongoing COVID-19 symptoms continued to show a reduction in memory scores. Our findings demonstrate that COVID-19 negatively impacts working memory function, but only in adults aged 25 years and over. Moreover, our results suggest that working memory deficits with COVID-19 can recov
Læs mere »
 World Antimicrobial Awareness Week 2022: What is the burden of antimicrobial resistance?As part of World Antimicrobial Resistance Week 2022, News-Medical speaks to Dr. Tomislav Meštrović about his new research discussing the burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in the WHO European region, as well as about how we can prevent antimicrobial resistance together.
World Antimicrobial Awareness Week 2022: What is the burden of antimicrobial resistance?As part of World Antimicrobial Resistance Week 2022, News-Medical speaks to Dr. Tomislav Meštrović about his new research discussing the burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in the WHO European region, as well as about how we can prevent antimicrobial resistance together.
Læs mere »
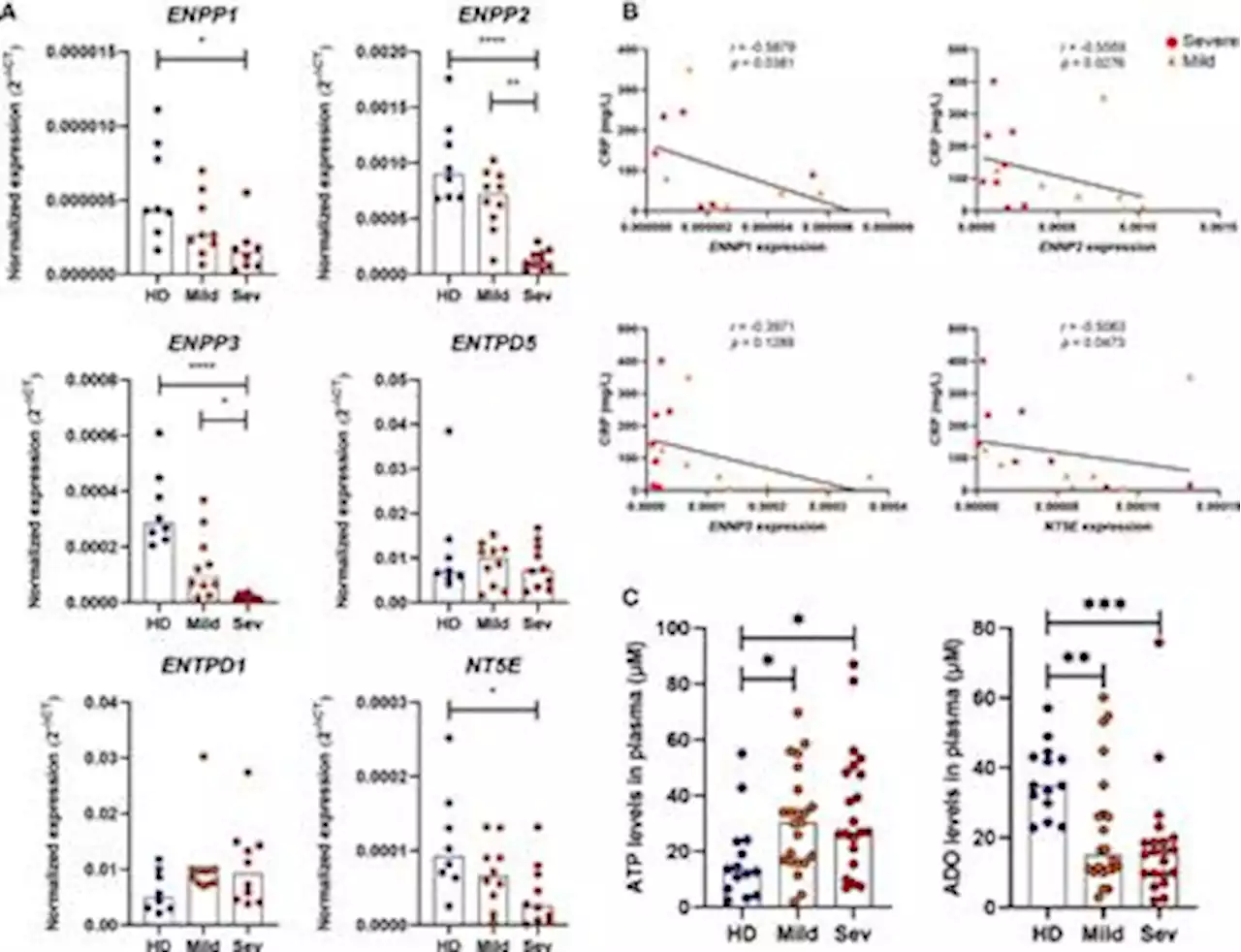 Frontiers | Dysfunctional purinergic signaling correlates with disease severity in COVID-19 patientsEctonucleotidases modulate inflammatory responses by balancing extracellular ATP and adenosine (ADO) and might be involved in COVID-19 immunopathogenesis. Here, we explored the contribution of extracellular nucleotides metabolism to COVID-19 severity in mild and severe cases of the disease. We verified that the gene expression of ectonucleotidases is reduced in the whole blood of patients with COVID-19 and is negatively correlated to CRP plasma levels, an inflammatory marker of disease severity. In line with these findings, COVID-19 patients present higher ATP levels in plasma and reduced levels of ADO when compared to healthy controls. Cell type-specific analysis revealed higher frequencies of CD39+ T cells in severely ill patients, while CD4+ and CD8+ expressing CD73 are reduced in this same group. The frequency of B cells CD39+CD73+ is also decreased during acute COVID-19. Interestingly, B cells from COVID-19 patients showed a reduced capacity to hydrolyze ATP into ADP and ADO. Furthermore, impaired expression of ADO receptors and a compromised activation of its signaling pathway is observed in COVID-19 patients. The presence of ADO in vitro, however, suppressed inflammatory responses triggered in patients’ cells. In summary, our findings support the idea that alterations in the metabolism of extracellular purines contribute to immune dysregulation during COVID-19, possibly favoring disease severity, and suggest that ADO may be a therapeutic approach for the disease.
Frontiers | Dysfunctional purinergic signaling correlates with disease severity in COVID-19 patientsEctonucleotidases modulate inflammatory responses by balancing extracellular ATP and adenosine (ADO) and might be involved in COVID-19 immunopathogenesis. Here, we explored the contribution of extracellular nucleotides metabolism to COVID-19 severity in mild and severe cases of the disease. We verified that the gene expression of ectonucleotidases is reduced in the whole blood of patients with COVID-19 and is negatively correlated to CRP plasma levels, an inflammatory marker of disease severity. In line with these findings, COVID-19 patients present higher ATP levels in plasma and reduced levels of ADO when compared to healthy controls. Cell type-specific analysis revealed higher frequencies of CD39+ T cells in severely ill patients, while CD4+ and CD8+ expressing CD73 are reduced in this same group. The frequency of B cells CD39+CD73+ is also decreased during acute COVID-19. Interestingly, B cells from COVID-19 patients showed a reduced capacity to hydrolyze ATP into ADP and ADO. Furthermore, impaired expression of ADO receptors and a compromised activation of its signaling pathway is observed in COVID-19 patients. The presence of ADO in vitro, however, suppressed inflammatory responses triggered in patients’ cells. In summary, our findings support the idea that alterations in the metabolism of extracellular purines contribute to immune dysregulation during COVID-19, possibly favoring disease severity, and suggest that ADO may be a therapeutic approach for the disease.
Læs mere »
 England stars not allowed to see stunning Wags at World Cup over Covid fearsENGLAND players could meet their families after Friday’s United States match – but it depends on Covid rates in Qatar. Manager Gareth Southgate is hoping that the 26-man squad could have a pr…
England stars not allowed to see stunning Wags at World Cup over Covid fearsENGLAND players could meet their families after Friday’s United States match – but it depends on Covid rates in Qatar. Manager Gareth Southgate is hoping that the 26-man squad could have a pr…
Læs mere »
 World Antimicrobial Awareness Week 2022: The Antibiotic Footprint of FarmingWe spoke to Coilin Nuna, the Scientific Advisor for the Alliance to Save our Antibiotics, about how antibiotics are used in farming and why the overuse of antibiotics in farming contributes to the problem of antimicrobial resistance.
World Antimicrobial Awareness Week 2022: The Antibiotic Footprint of FarmingWe spoke to Coilin Nuna, the Scientific Advisor for the Alliance to Save our Antibiotics, about how antibiotics are used in farming and why the overuse of antibiotics in farming contributes to the problem of antimicrobial resistance.
Læs mere »
