Researchers hope it could help diagnose illnesses in youngsters faster, and tackle the overuse of antibiotics.
The test could identify the cause of a fever in children in under one hour
However, a global team led by researchers from Imperial College London has explored the potential to identify how genes in the blood respond to certain infections and diseases to diagnose illnesses faster and tackle the overuse of antibiotics. Machine learning was then applied to recognise which patterns were related to specific conditions, focusing on 161 genes.
It is hoped the new test could tackle the overuse of antibiotics in children, which are usually prescribed until an antibacterial infection can be ruled out. “Such delays can stop patients getting the right treatment early on, so there is a clear and urgent need to improve diagnostics. Using this new approach, once it’s translated to near point-of- care devices, could be transformative for healthcare.”
“With this initial proof-of-concept study, we’ve been able to show that our multi-disease, machine-learning diagnostic approach works. This kind of advance is only possible through interdisciplinary collaboration and large research consortia, which bring together expertise from infectious disease, molecular science, and bioinformatics.”
Danmark Seneste Nyt, Danmark Overskrifter
Similar News:Du kan også læse nyheder, der ligner denne, som vi har indsamlet fra andre nyhedskilder.
 ‘Transformative’ blood test can identify cause of fever in children in an hourResearchers hope it could help diagnose illnesses in youngsters faster, and tackle the overuse of antibiotics.
‘Transformative’ blood test can identify cause of fever in children in an hourResearchers hope it could help diagnose illnesses in youngsters faster, and tackle the overuse of antibiotics.
Læs mere »
 Researchers find genetic cause of Raynaud's phenomenonResearchers at Queen Mary University of London's Precision Healthcare Research Institute (PHURI) and the Berlin Institute of Health (BIH) at Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin have identified the genetic causes of Raynaud's phenomenon. Their findings, published today in Nature Communications, could lead to the first effective treatments for people with Raynaud's.
Researchers find genetic cause of Raynaud's phenomenonResearchers at Queen Mary University of London's Precision Healthcare Research Institute (PHURI) and the Berlin Institute of Health (BIH) at Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin have identified the genetic causes of Raynaud's phenomenon. Their findings, published today in Nature Communications, could lead to the first effective treatments for people with Raynaud's.
Læs mere »
 Researchers discover contrast dye shortage affected assessment of stroke patientsUniversity of Missouri School of Medicine neurologist Adnan Qureshi, MD recently led a study that discovered last year's iodinated media contrast dye shortage affected the assessment of stroke patients at hospitals across the country. Injecting or drinking the media contrast helps doctors see blood vessels and organs more clearly in an X-ray or a computed tomography (CT) scan.
Researchers discover contrast dye shortage affected assessment of stroke patientsUniversity of Missouri School of Medicine neurologist Adnan Qureshi, MD recently led a study that discovered last year's iodinated media contrast dye shortage affected the assessment of stroke patients at hospitals across the country. Injecting or drinking the media contrast helps doctors see blood vessels and organs more clearly in an X-ray or a computed tomography (CT) scan.
Læs mere »
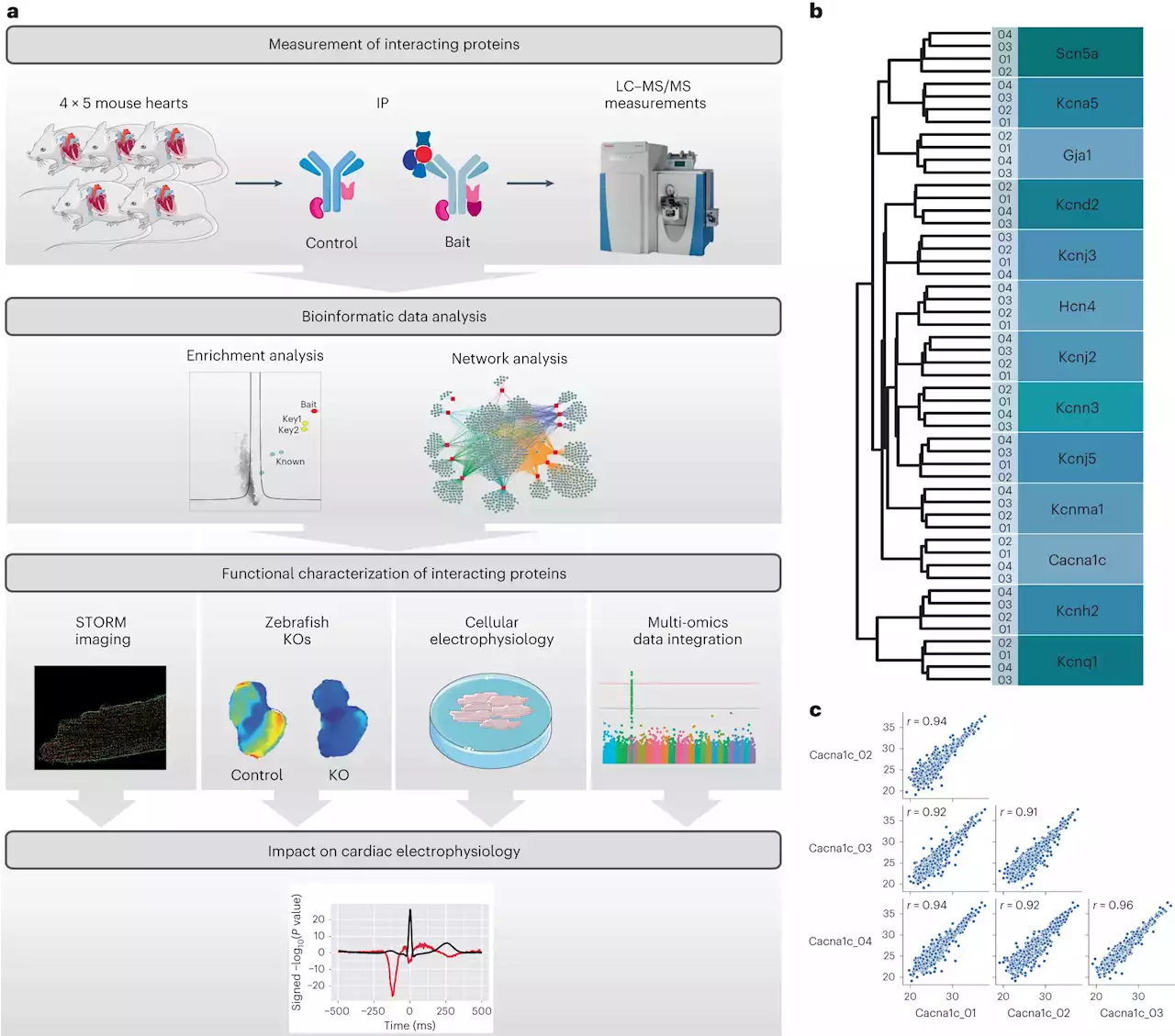 Researchers find heartbeat relies on surprisingly large network of proteinsThe first mapping of the heart's crucial ion channels reveals a surprisingly extensive network of proteins. This understanding is the first step towards more precise treatment for patients with cardiac arrhythmias.
Researchers find heartbeat relies on surprisingly large network of proteinsThe first mapping of the heart's crucial ion channels reveals a surprisingly extensive network of proteins. This understanding is the first step towards more precise treatment for patients with cardiac arrhythmias.
Læs mere »
 Researchers develop new rapid and reliable method for SARS-CoV-2 detectionCommercially available mass spectrometers can reliably detect the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. In the journal 'Clinical proteomics' researchers from the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) present a new method which employs equipment that is already being used in hospitals and laboratories to detect bacterial and fungal infections.
Researchers develop new rapid and reliable method for SARS-CoV-2 detectionCommercially available mass spectrometers can reliably detect the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. In the journal 'Clinical proteomics' researchers from the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) present a new method which employs equipment that is already being used in hospitals and laboratories to detect bacterial and fungal infections.
Læs mere »
Cyber security researchers become target of criminal hackers\n\t\t\tKeep abreast of significant corporate, financial and political developments around the world.\n\t\t\tStay informed and spot emerging risks and opportunities with independent global reporting, expert\n\t\t\tcommentary and analysis you can trust.\n\t\t
Læs mere »
