Researchers evaluated distinct immune responses to mRNA and vector-based COVID-19 vaccines and natural SARS-CoV-2 infections.
By Neha MathurAug 17 2023Reviewed by Sophia Coveney In a recent article published in Scientific Reports, researchers evaluated distinct immune responses to messenger ribonucleic acid and vector-based coronavirus disease 2019 vaccines, and natural severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infections.
IgG is the most abundant immunoglobulin isotype in human serum. Each subclass of IgG has a unique profile related to antigen binding, immune complex formation, complement activation, and triggering of effector cell activation. In another study, it was suggested that adenovirus-based vaccines do not elicit a long-term S-specific IgG4 response.
The team collected serum samples on median day 128 post-booster vaccination and from CONV and HOSP patients on median days 54 and 21, respectively. They also monitored 15 mRNA-vaccinated volunteers on median days 37 and 160 post-booster. Regarding the pattern of IgG subclasses, it was comparable for individuals infected before mRNA vaccinations and those who received vector-based vaccines, and even for COVID-19 patients who received no vaccine. COVID-19 patients predominantly had S-specific IgG1/G3 subclasses in serum on the median of 21 days post-infection.
Danmark Seneste Nyt, Danmark Overskrifter
Similar News:Du kan også læse nyheder, der ligner denne, som vi har indsamlet fra andre nyhedskilder.
 Researchers develop new rapid and reliable method for SARS-CoV-2 detectionCommercially available mass spectrometers can reliably detect the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. In the journal 'Clinical proteomics' researchers from the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) present a new method which employs equipment that is already being used in hospitals and laboratories to detect bacterial and fungal infections.
Researchers develop new rapid and reliable method for SARS-CoV-2 detectionCommercially available mass spectrometers can reliably detect the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. In the journal 'Clinical proteomics' researchers from the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) present a new method which employs equipment that is already being used in hospitals and laboratories to detect bacterial and fungal infections.
Læs mere »
 A study of links between fracking and health issues will be released by Pennsylvania researchersResearchers in heavily drilled Pennsylvania were preparing Tuesday to release findings from taxpayer-financed studies on possible links between the natural gas industry and pediatric cancer, asthma and poor birth outcomes.
A study of links between fracking and health issues will be released by Pennsylvania researchersResearchers in heavily drilled Pennsylvania were preparing Tuesday to release findings from taxpayer-financed studies on possible links between the natural gas industry and pediatric cancer, asthma and poor birth outcomes.
Læs mere »
 Study uses genomic data to produce high-resolution serial interval estimates for COVID-19Researchers developed an approach for integrating whole-genomic viral sequences and epidemiological information for serial interval (SI) estimation.
Study uses genomic data to produce high-resolution serial interval estimates for COVID-19Researchers developed an approach for integrating whole-genomic viral sequences and epidemiological information for serial interval (SI) estimation.
Læs mere »
 Kessler Foundation researchers receive $1.7 million in grants to improve lives of TBI patientsKessler Foundation scientists received four grants from the New Jersey Commission on Brain Injury Research, totaling nearly $1.7 million for studies based on a variety of novel approaches aimed at improving the lives of individuals with traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Kessler Foundation researchers receive $1.7 million in grants to improve lives of TBI patientsKessler Foundation scientists received four grants from the New Jersey Commission on Brain Injury Research, totaling nearly $1.7 million for studies based on a variety of novel approaches aimed at improving the lives of individuals with traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Læs mere »
 Neanderthals, environment, and evolution behind SARS-CoV-2 immune responsesResearch led by the Université Paris Cité, CNRS, France, has investigated factors driving variability in diverse immune responses to SARS-CoV-2.
Neanderthals, environment, and evolution behind SARS-CoV-2 immune responsesResearch led by the Université Paris Cité, CNRS, France, has investigated factors driving variability in diverse immune responses to SARS-CoV-2.
Læs mere »
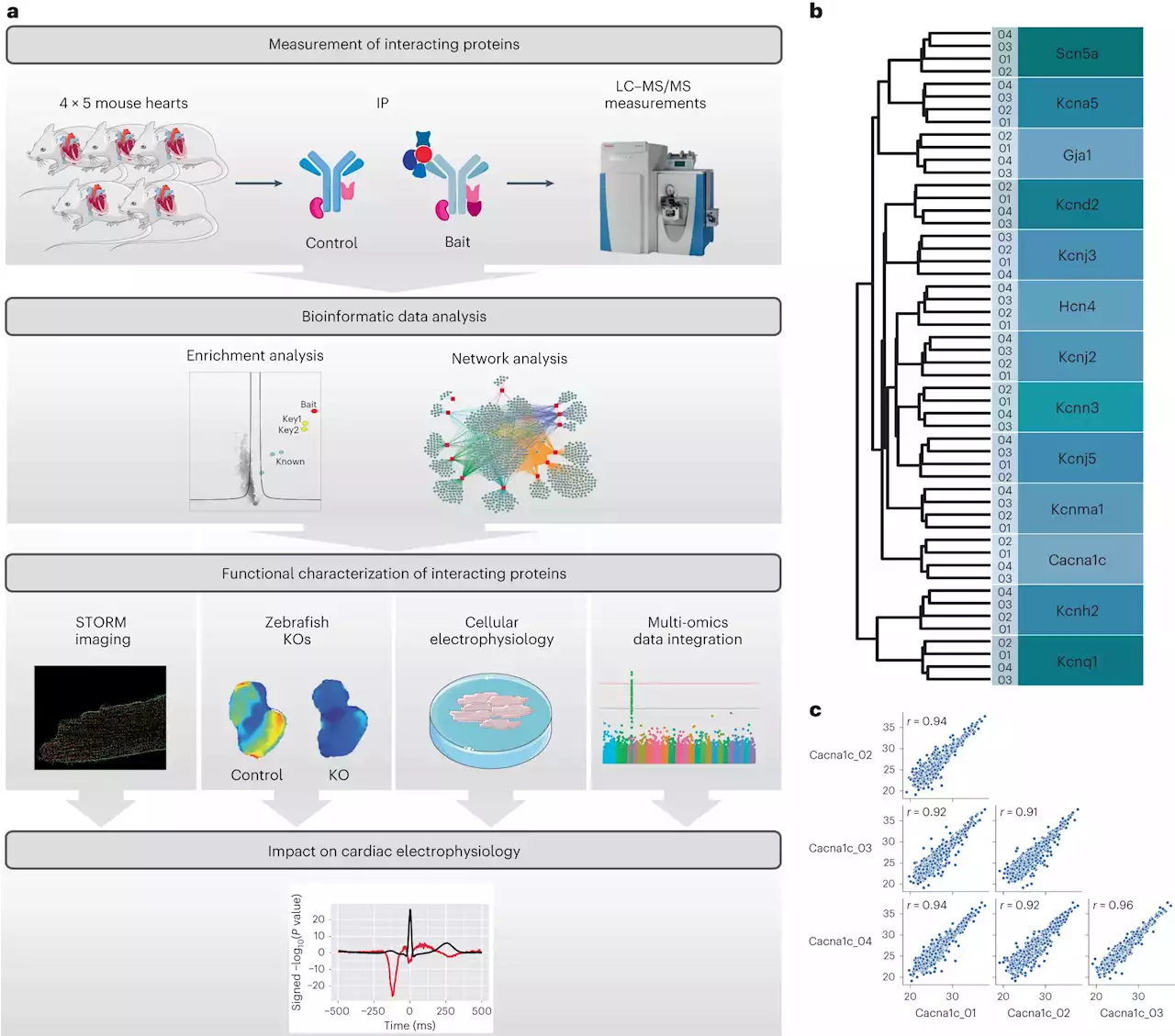 Researchers find heartbeat relies on surprisingly large network of proteinsThe first mapping of the heart's crucial ion channels reveals a surprisingly extensive network of proteins. This understanding is the first step towards more precise treatment for patients with cardiac arrhythmias.
Researchers find heartbeat relies on surprisingly large network of proteinsThe first mapping of the heart's crucial ion channels reveals a surprisingly extensive network of proteins. This understanding is the first step towards more precise treatment for patients with cardiac arrhythmias.
Læs mere »
