Study results provide strong evidence for association of genetic markers to long COVID mappable to fatigue UniWestminster QMUL longcovid COVID19 coronavirus covid genetics geneticmarker fatigue tired health
By Dr. Chinta SidharthanMar 2 2023Reviewed by Danielle Ellis, B.Sc. *Important notice: Research Square publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
The commonly reported symptoms include fever, headaches, debilitating fatigue, post-exertional malaise, dyspnea, loss of taste and smell, cognitive impairments such as difficulty concentrating, and other problems related to the cardiovascular, digestive, and renal systems. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has expressed the importance of expanding our understanding of the demographic and genetic risk factors associated with long COVID.
Blood samples were collected and subjected to low-pass whole genome sequencing. The participant selection ensured that the patients were not related to one another and their ancestries were evaluated. A control group consisting of available genomes of subpopulations of Iberian Spanish ancestry was also included in the study.
Furthermore, the distribution of depression-associated polygenic risk scores in the control samples showed a lower predisposition to suffer from depression than in the long COVID samples, indicating that depression was significant in predicting long COVID susceptibility.
Danmark Seneste Nyt, Danmark Overskrifter
Similar News:Du kan også læse nyheder, der ligner denne, som vi har indsamlet fra andre nyhedskilder.
 Efficacy of first dose of covid-19 vaccine versus no vaccination on symptoms of patients with long covid: target trial emulation based on ComPaRe e-cohortObjective To evaluate the effect of covid-19 vaccination on the severity of symptoms in patients with long covid. Design Target trial emulation based on ComPaRe e-cohort. Data source ComPaRe long covid cohort, a nationwide e-cohort (ie, a cohort where recruitment and follow-up are performed online) of patients with long covid, in France. Methods Adult patients (aged ≥18 years) enrolled in the ComPaRe cohort before 1 May 2021 were included in the study if they reported a confirmed or suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection, symptoms persistent for |3 weeks after onset, and at least one symptom attributable to long covid at baseline. Patients who received a first covid-19 vaccine injection were matched with an unvaccinated control group in a 1:1 ratio according to their propensity scores. Number of long covid symptoms, rate of complete remission of long covid, and proportion of patients reporting an unacceptable symptom state at 120 days were recorded. Results 910 patients were included in the analyses (455 in the vaccinated group and 455 in the control group). By 120 days, vaccination had reduced the number of long covid symptoms (mean 13.0 (standard deviation 9.4) in the vaccinated group v 14.8 (9.8) in the control group; mean difference −1.8, 95% confidence interval −3.0 to −0.5) and doubled the rate of patients in remission (16.6% v 7.5%, hazard ratio 1.93, 95% confidence interval 1.18 to 3.14). Vaccination reduced the effect of long covid on patients' lives (mean score on the impact tool 24.3 (standard deviation 16.7) v 27.6 (16.7); mean difference −3.3, 95% confidence interval −5.7 to −1.0) and the proportion of patients with an unacceptable symptom state (38.9% v 46.4%, risk difference −7.4%, 95% confidence interval −14.5% to −0.3%). In the vaccinated group, two (0.4%) patients reported serious adverse events requiring admission to hospital. Conclusion In this study, covid-19 vaccination reduced the severity of symptoms and the effect of long covid on patients' social,
Efficacy of first dose of covid-19 vaccine versus no vaccination on symptoms of patients with long covid: target trial emulation based on ComPaRe e-cohortObjective To evaluate the effect of covid-19 vaccination on the severity of symptoms in patients with long covid. Design Target trial emulation based on ComPaRe e-cohort. Data source ComPaRe long covid cohort, a nationwide e-cohort (ie, a cohort where recruitment and follow-up are performed online) of patients with long covid, in France. Methods Adult patients (aged ≥18 years) enrolled in the ComPaRe cohort before 1 May 2021 were included in the study if they reported a confirmed or suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection, symptoms persistent for |3 weeks after onset, and at least one symptom attributable to long covid at baseline. Patients who received a first covid-19 vaccine injection were matched with an unvaccinated control group in a 1:1 ratio according to their propensity scores. Number of long covid symptoms, rate of complete remission of long covid, and proportion of patients reporting an unacceptable symptom state at 120 days were recorded. Results 910 patients were included in the analyses (455 in the vaccinated group and 455 in the control group). By 120 days, vaccination had reduced the number of long covid symptoms (mean 13.0 (standard deviation 9.4) in the vaccinated group v 14.8 (9.8) in the control group; mean difference −1.8, 95% confidence interval −3.0 to −0.5) and doubled the rate of patients in remission (16.6% v 7.5%, hazard ratio 1.93, 95% confidence interval 1.18 to 3.14). Vaccination reduced the effect of long covid on patients' lives (mean score on the impact tool 24.3 (standard deviation 16.7) v 27.6 (16.7); mean difference −3.3, 95% confidence interval −5.7 to −1.0) and the proportion of patients with an unacceptable symptom state (38.9% v 46.4%, risk difference −7.4%, 95% confidence interval −14.5% to −0.3%). In the vaccinated group, two (0.4%) patients reported serious adverse events requiring admission to hospital. Conclusion In this study, covid-19 vaccination reduced the severity of symptoms and the effect of long covid on patients' social,
Læs mere »
 Study: US government catalyzed and substantially invested in mRNA COVID-19 vaccine development over decadesIn the 35 years before the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. government invested at least $337 million into critical research that led to the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, according to a study published by The BMJ today.
Study: US government catalyzed and substantially invested in mRNA COVID-19 vaccine development over decadesIn the 35 years before the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. government invested at least $337 million into critical research that led to the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, according to a study published by The BMJ today.
Læs mere »
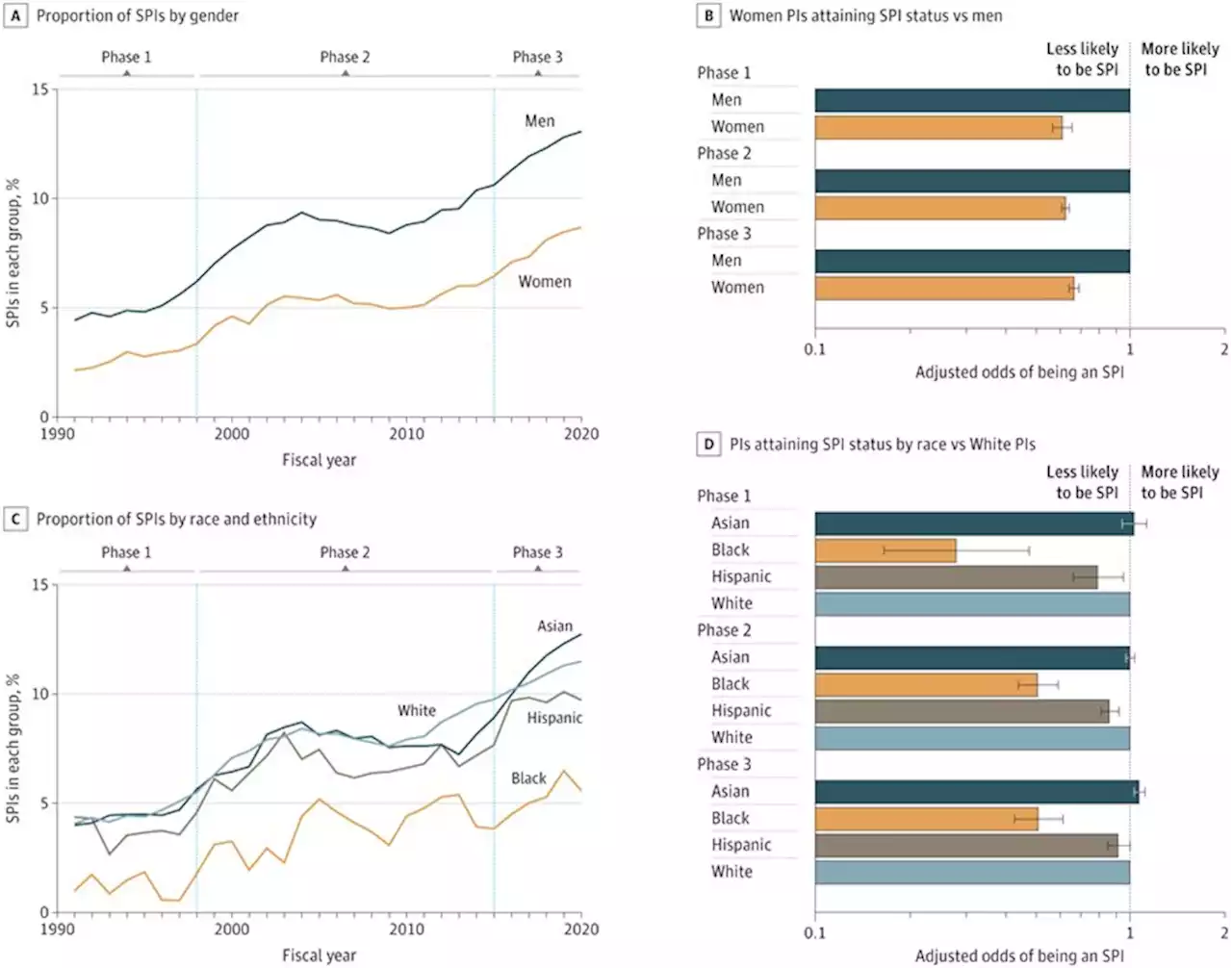 Black and women scientists are less likely to have multiple research grants, finds studyA growing number of researchers have more than two grants simultaneously from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), but women and Black researchers are less likely than white men to be among them, a new Yale study finds. This disparity, the researchers say, has implications for research innovation and public trust and can impact career trajectories.
Black and women scientists are less likely to have multiple research grants, finds studyA growing number of researchers have more than two grants simultaneously from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), but women and Black researchers are less likely than white men to be among them, a new Yale study finds. This disparity, the researchers say, has implications for research innovation and public trust and can impact career trajectories.
Læs mere »
 Daily 11-minute brisk walk is enough to reduce risk of early death, say researchersOne in ten early deaths could be prevented if everyone managed at least half the recommended level of physical activity, say a team led by researchers at the University of Cambridge.
Daily 11-minute brisk walk is enough to reduce risk of early death, say researchersOne in ten early deaths could be prevented if everyone managed at least half the recommended level of physical activity, say a team led by researchers at the University of Cambridge.
Læs mere »
 Through the eye of the beholder: Researchers find people with autism process illusory shapes differentlyThere is this picture—you may have seen it. It is black and white and has two silhouettes facing one another. Or maybe you see the black vase with a white background. But now, you likely see both.
Through the eye of the beholder: Researchers find people with autism process illusory shapes differentlyThere is this picture—you may have seen it. It is black and white and has two silhouettes facing one another. Or maybe you see the black vase with a white background. But now, you likely see both.
Læs mere »
 COVID-19 bacteremic co-infection is a major risk factor for mortality, ICU admission, and mechanical ventilation - Critical CareBackground Recent single-center reports have suggested that community-acquired bacteremic co-infection in the context of Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) may be an important driver of mortality; however, these reports have not been validated with a multicenter, demographically diverse, cohort study with data spanning the pandemic. Methods In this multicenter, retrospective cohort study, inpatient encounters were assessed for COVID-19 with community-acquired bacteremic co-infection using 48-h post-admission blood cultures and grouped by: (1) confirmed co-infection [recovery of bacterial pathogen], (2) suspected co-infection [negative culture with ≥ 2 antimicrobials administered], and (3) no evidence of co-infection [no culture]. The primary outcomes were in-hospital mortality, ICU admission, and mechanical ventilation. COVID-19 bacterial co-infection risk factors and impact on primary outcomes were determined using multivariate logistic regressions and expressed as adjusted odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals (Cohort, OR 95% CI, Wald test p value). Results The studied cohorts included 13,781 COVID-19 inpatient encounters from 2020 to 2022 in the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB, n = 4075) and Ochsner Louisiana State University Health—Shreveport (OLHS, n = 9706) cohorts with confirmed (2.5%), suspected (46%), or no community-acquired bacterial co-infection (51.5%) and a comparison cohort consisting of 99,170 inpatient encounters from 2010 to 2019 (UAB pre-COVID-19 pandemic cohort). Significantly increased likelihood of COVID-19 bacterial co-infection was observed in patients with elevated ≥ 15 neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (UAB: 1.95 [1.21–3.07]; OLHS: 3.65 [2.66–5.05], p | 0.001 for both) within 48-h of hospital admission. Bacterial co-infection was found to confer the greatest increased risk for in-hospital mortality (UAB: 3.07 [2.42–5.46]; OLHS: 4.05 [2.29–6.97], p | 0.001 for both), ICU admission (UAB: 4.47 [2.87–7.09], OLHS: 2.65 [2.00–3.48], p
COVID-19 bacteremic co-infection is a major risk factor for mortality, ICU admission, and mechanical ventilation - Critical CareBackground Recent single-center reports have suggested that community-acquired bacteremic co-infection in the context of Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) may be an important driver of mortality; however, these reports have not been validated with a multicenter, demographically diverse, cohort study with data spanning the pandemic. Methods In this multicenter, retrospective cohort study, inpatient encounters were assessed for COVID-19 with community-acquired bacteremic co-infection using 48-h post-admission blood cultures and grouped by: (1) confirmed co-infection [recovery of bacterial pathogen], (2) suspected co-infection [negative culture with ≥ 2 antimicrobials administered], and (3) no evidence of co-infection [no culture]. The primary outcomes were in-hospital mortality, ICU admission, and mechanical ventilation. COVID-19 bacterial co-infection risk factors and impact on primary outcomes were determined using multivariate logistic regressions and expressed as adjusted odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals (Cohort, OR 95% CI, Wald test p value). Results The studied cohorts included 13,781 COVID-19 inpatient encounters from 2020 to 2022 in the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB, n = 4075) and Ochsner Louisiana State University Health—Shreveport (OLHS, n = 9706) cohorts with confirmed (2.5%), suspected (46%), or no community-acquired bacterial co-infection (51.5%) and a comparison cohort consisting of 99,170 inpatient encounters from 2010 to 2019 (UAB pre-COVID-19 pandemic cohort). Significantly increased likelihood of COVID-19 bacterial co-infection was observed in patients with elevated ≥ 15 neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (UAB: 1.95 [1.21–3.07]; OLHS: 3.65 [2.66–5.05], p | 0.001 for both) within 48-h of hospital admission. Bacterial co-infection was found to confer the greatest increased risk for in-hospital mortality (UAB: 3.07 [2.42–5.46]; OLHS: 4.05 [2.29–6.97], p | 0.001 for both), ICU admission (UAB: 4.47 [2.87–7.09], OLHS: 2.65 [2.00–3.48], p
Læs mere »
