Study reports the first protein-based diagnostic signature to discriminate MIS-C from Kawasaki Disease and other common infections virus infection disease diganosis LivUni uniofwarwick imperialcollege
By Dr. Liji Thomas, MDAug 4 2023Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. The coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic was widely understood to spare children, both in terms of the number of infections and severity of disease. Nevertheless, children continue to be infected with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 , with a significant minority of patients experiencing severe symptoms in the form of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children .
Introduction While MIS-C is established as a clinical diagnosis, there remains a lack of information on the pathogenesis of this condition. Also known as pediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome temporally associated with COVID-19 , MIS-C typically arises two to six weeks following SARS-CoV-2 infection in children.
About the study To develop guidelines that will discriminate between these conditions, the researchers of the current study analyzed a set of different plasma proteins to identify those that could be used as biomarkers of MIS-C but not other similar illnesses. Related StoriesUsing these three biomarkers, the researchers successfully distinguished seven out of eight cases of MIS-C from other similar conditions. This combination was optimal for this purpose as compared to the use of any two markers.
CD163, which is a scavenger protein that is found in its soluble form when shed during inflammation, is often raised in SARS-CoV-2 infection in children. Likewise, CD163 levels also rise with macrophage activation, thus corroborating its assigned value as an indicator of critically severe MIS-C.
Danmark Seneste Nyt, Danmark Overskrifter
Similar News:Du kan også læse nyheder, der ligner denne, som vi har indsamlet fra andre nyhedskilder.
 US issues warning over incurable mystery diseaseAs many as 450,000 people may have an undiagnosed tick-borne disease that can cause allergic reactions to red meat.
US issues warning over incurable mystery diseaseAs many as 450,000 people may have an undiagnosed tick-borne disease that can cause allergic reactions to red meat.
Læs mere »
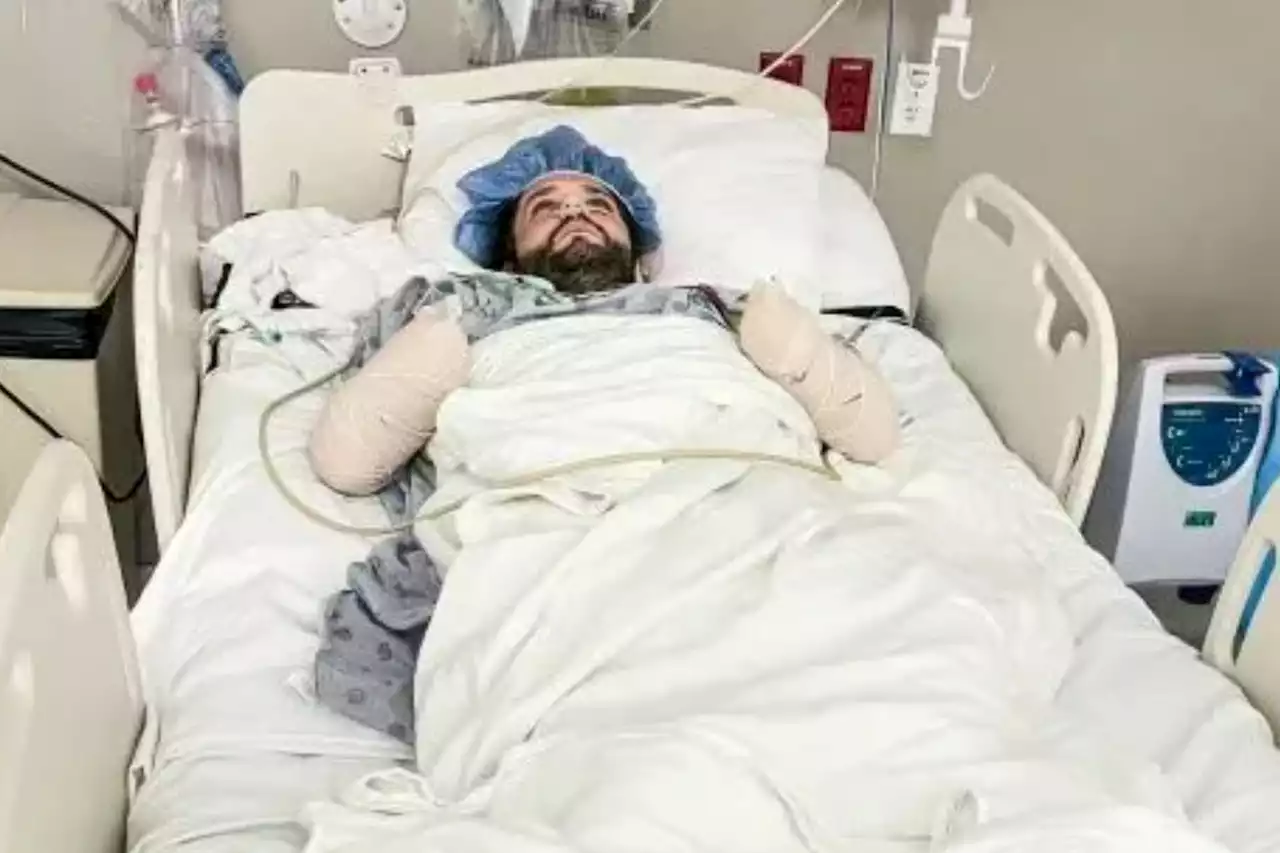 Doctors discover flea bite left man riddled with killer disease from middle agesDOCTORS were shocked to discover a tick bite left a man with a killer disease dating back to the middle ages. Michael Kohlhof, 35, was taken to hospital in Texas, US in June after developing flu-li…
Doctors discover flea bite left man riddled with killer disease from middle agesDOCTORS were shocked to discover a tick bite left a man with a killer disease dating back to the middle ages. Michael Kohlhof, 35, was taken to hospital in Texas, US in June after developing flu-li…
Læs mere »
 Gigi Hadid Shares Update On Sister Bella's Treatment For Lyme DiseaseBella Hadid has publicly discussed her struggles with the tick-borne disease on several occasions.
Gigi Hadid Shares Update On Sister Bella's Treatment For Lyme DiseaseBella Hadid has publicly discussed her struggles with the tick-borne disease on several occasions.
Læs mere »
 Gross habit millions of Brits have could increase risk of catching nasty diseaseA GROSS habit that millions of Brits have could increase the risk of catching a deadly disease, it has been revealed. Dutch researchers have found that a seemingly innocent, if frowned-upon, behavi…
Gross habit millions of Brits have could increase risk of catching nasty diseaseA GROSS habit that millions of Brits have could increase the risk of catching a deadly disease, it has been revealed. Dutch researchers have found that a seemingly innocent, if frowned-upon, behavi…
Læs mere »
 Can genome editing transform ocular disease treatment?Can genome editing transform ocular disease treatment? Nature UCIrvine ocular oculardisease eyedisease genetics genomeediting geneediting
Can genome editing transform ocular disease treatment?Can genome editing transform ocular disease treatment? Nature UCIrvine ocular oculardisease eyedisease genetics genomeediting geneediting
Læs mere »
 Machine learning in neurodegenerative disease research: a growing trendMachine learning in neurodegenerative disease research: a growing trend medrxivpreprint mcgillu machinelearning neurodegnerative neurdegenerativedisease disease
Machine learning in neurodegenerative disease research: a growing trendMachine learning in neurodegenerative disease research: a growing trend medrxivpreprint mcgillu machinelearning neurodegnerative neurdegenerativedisease disease
Læs mere »
