Researchers at DZNE and Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin have pioneered a novel treatment for the most common autoimmune encephalitis.
Reviewed by Danielle Ellis, B.Sc.Nov 3 2023 By reprogramming white blood cells to target and eliminate disease-causing cells, the approach offers a new level of precision and efficiency. The technique has proven successful in laboratory studies, clinical trials in humans are already being planned.
New treatment method Around 200 to 300 people are estimated to develop NMDA receptor encephalitis in Germany every year - with severe symptoms: They experience memory impairment, epileptic seizures, impaired consciousness, and psychosis. Severe cases may even require treatment in an intensive care unit. The new procedure would be an enormous improvement over current therapy.
Reprogrammed cells For their new, targeted therapy, the researchers had to develop an elaborate procedure: "We use human T cells, which we can obtain from patients' blood, and modify them by adding a coupling molecule," explains Dr. Momsen Reincke, one of the study's first authors, who also researches at DZNE and Charité. This genetic reprogramming turns the T cells - a special type of white blood cells - into what is known as CAAR T cells.
Danmark Seneste Nyt, Danmark Overskrifter
Similar News:Du kan også læse nyheder, der ligner denne, som vi har indsamlet fra andre nyhedskilder.
 Researchers discover new mechanism of cancer treatment resistanceA surprising mechanism that makes some cancers treatment-resistant has been discovered by Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian investigators.
Researchers discover new mechanism of cancer treatment resistanceA surprising mechanism that makes some cancers treatment-resistant has been discovered by Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian investigators.
Læs mere »
 Tufts researchers explore the science of agingAnti-wrinkle creams, superfoods that keep you young, dietary supplements that promise improved memory, 'immortal' cells that can renew themselves forever-;in our stores and media, claims about aging abound.
Tufts researchers explore the science of agingAnti-wrinkle creams, superfoods that keep you young, dietary supplements that promise improved memory, 'immortal' cells that can renew themselves forever-;in our stores and media, claims about aging abound.
Læs mere »
 AI bot capable of insider trading and lying, say researchersThe researchers behind the simulation say there is a risk of this happening for real in the future.
AI bot capable of insider trading and lying, say researchersThe researchers behind the simulation say there is a risk of this happening for real in the future.
Læs mere »
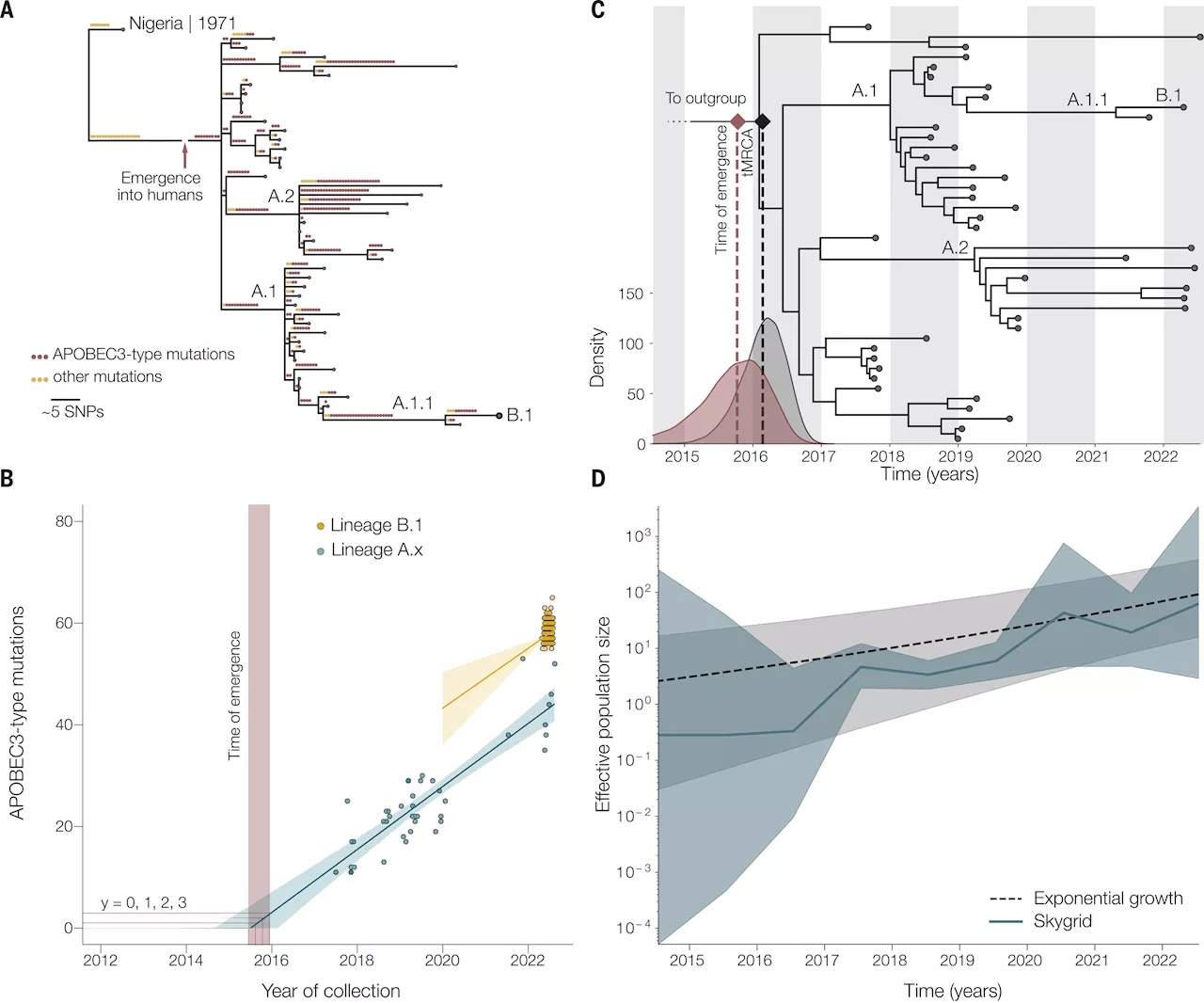 Researchers find evidence of mpox circulating in humans since 2016A large international team of medical researchers and epidemiologists has found evidence that monkeypox (mpox) has been circulating in humans since 2016. In their study, reported in the journal Science, the group used Bayesian evolutionary analysis of the mpox virus to show that its genomic history includes years of change due to human infections.
Researchers find evidence of mpox circulating in humans since 2016A large international team of medical researchers and epidemiologists has found evidence that monkeypox (mpox) has been circulating in humans since 2016. In their study, reported in the journal Science, the group used Bayesian evolutionary analysis of the mpox virus to show that its genomic history includes years of change due to human infections.
Læs mere »
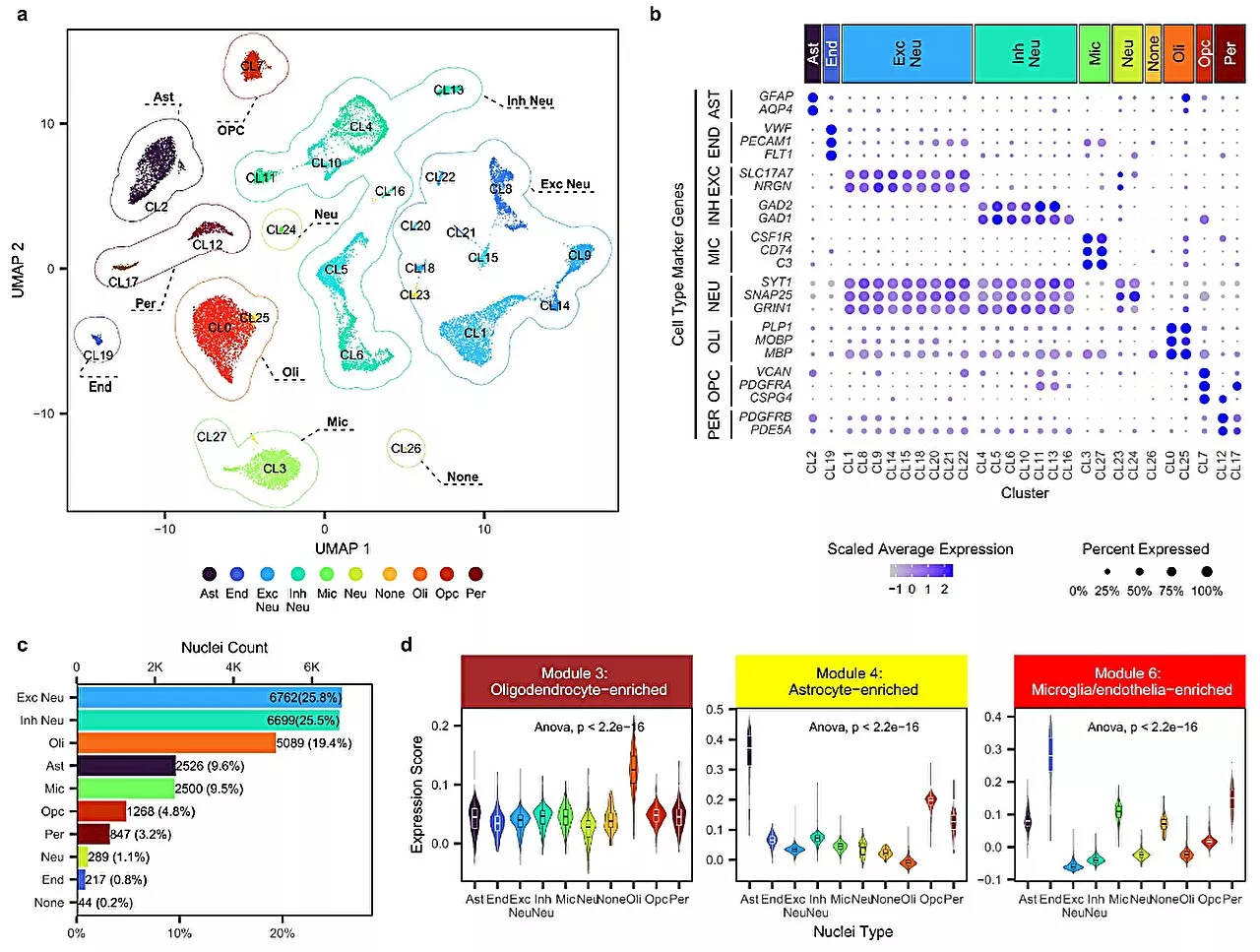 Researchers discover new molecular drug targets for progressive neurological disorderThere is no cure for progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), a brain disorder marked by walking and balance difficulties. Its symptoms also mimic Parkinson's disease and dementia. The condition leads to rapid, progressive decline and death.
Researchers discover new molecular drug targets for progressive neurological disorderThere is no cure for progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), a brain disorder marked by walking and balance difficulties. Its symptoms also mimic Parkinson's disease and dementia. The condition leads to rapid, progressive decline and death.
Læs mere »
 Researchers say early warnings could prevent thunderstorm asthma eventsMelbourne lays claim to the unwanted title of being the epicenter of epidemic thunderstorm asthma (ETSA) worldwide, having experienced seven of the 26 recorded events.
Researchers say early warnings could prevent thunderstorm asthma eventsMelbourne lays claim to the unwanted title of being the epicenter of epidemic thunderstorm asthma (ETSA) worldwide, having experienced seven of the 26 recorded events.
Læs mere »
