People who have had a heart attack often report pain about a year later. Moderate or extreme pain after a heart attack – most commonly pain due to other health conditions – may help predict the likelihood of death over the next 8.5 years, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access, peer-reviewed journal of the American Heart Association.
In this study, participants who said they had extreme pain after a heart attack were more than twice as likely to die during the study period compared to those who reported no pain.
Linda Vixner, P.T., Ph.D., study author, associate professor of medical science at the School of Health and Welfare at Dalarna University in Falun, Sweden
Danmark Seneste Nyt, Danmark Overskrifter
Similar News:Du kan også læse nyheder, der ligner denne, som vi har indsamlet fra andre nyhedskilder.
 Experiencing pain after a heart attack may predict long-term survivalPeople who have had a heart attack often report pain about a year later. Moderate or extreme pain after a heart attack—most commonly pain due to other health conditions—may help predict the likelihood of death over the next 8.5 years, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Experiencing pain after a heart attack may predict long-term survivalPeople who have had a heart attack often report pain about a year later. Moderate or extreme pain after a heart attack—most commonly pain due to other health conditions—may help predict the likelihood of death over the next 8.5 years, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Læs mere »
 These are the common signs of a heart attack which are often ignoredThe NHS is raising awareness of the symptoms and encouraging people to dial 999 as the number of admissions for heart attacks returns to pre-pandemic levels.
These are the common signs of a heart attack which are often ignoredThe NHS is raising awareness of the symptoms and encouraging people to dial 999 as the number of admissions for heart attacks returns to pre-pandemic levels.
Læs mere »
 The data vs driver conflict at the heart of F1's ground-effect carsThe introduction of Formula 1's new technical regulations caused a few doubts to be raised about the all-knowing power of data, as phenomenon like porpoising caught teams unaware. Such differences between the real and virtual world are now being examined to help squads maximise their car's potential
The data vs driver conflict at the heart of F1's ground-effect carsThe introduction of Formula 1's new technical regulations caused a few doubts to be raised about the all-knowing power of data, as phenomenon like porpoising caught teams unaware. Such differences between the real and virtual world are now being examined to help squads maximise their car's potential
Læs mere »
 Arterial stiffness may cause and worsen heart damage among adolescentsArterial stiffness is a novel cause of premature heart damage among adolescents, according to a new follow-up study. The study was conducted in collaboration between Texas Children's Hospital and Baylor College of Medicine in the U.S., the University of Bristol in the U.K., the University of Exeter in the U.K., and the University of Eastern Finland. The results were published in Atherosclerosis.
Arterial stiffness may cause and worsen heart damage among adolescentsArterial stiffness is a novel cause of premature heart damage among adolescents, according to a new follow-up study. The study was conducted in collaboration between Texas Children's Hospital and Baylor College of Medicine in the U.S., the University of Bristol in the U.K., the University of Exeter in the U.K., and the University of Eastern Finland. The results were published in Atherosclerosis.
Læs mere »
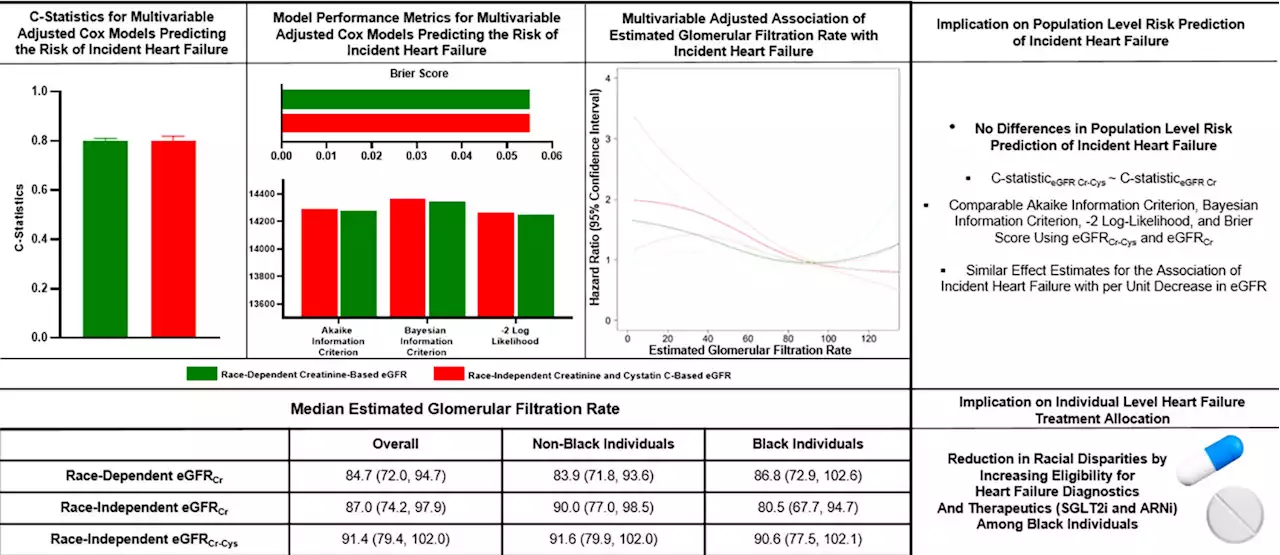 New kidney function equation may reduce health disparities, improve access to heart failure therapyPhysician-scientists from the University of Alabama at Birmingham Marnix E. Heersink School of Medicine recently conducted a large-scale analysis to assess the impact of a newly introduced equation used to evaluate one's heart failure risk. The study, published in the Journal of Cardiac Failure, showed that the new and old kidney function equations had comparable values in predicting the risk of heart failure.
New kidney function equation may reduce health disparities, improve access to heart failure therapyPhysician-scientists from the University of Alabama at Birmingham Marnix E. Heersink School of Medicine recently conducted a large-scale analysis to assess the impact of a newly introduced equation used to evaluate one's heart failure risk. The study, published in the Journal of Cardiac Failure, showed that the new and old kidney function equations had comparable values in predicting the risk of heart failure.
Læs mere »
