Kidney organoids provide a promising platform in vitro to model the mechanisms of kidney disease, however, they are limited by an existing lack of knowledge of their inherent functional protein expression. In a new report in Nature Communications, Martiz Lassé and a team of scientists in medicine and kidney health, in Denmark, Germany, and the U.S., defined the organoid proteome and their transcriptome trajectories during culture, and upon exposure to the tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα); a cytokine stressor.
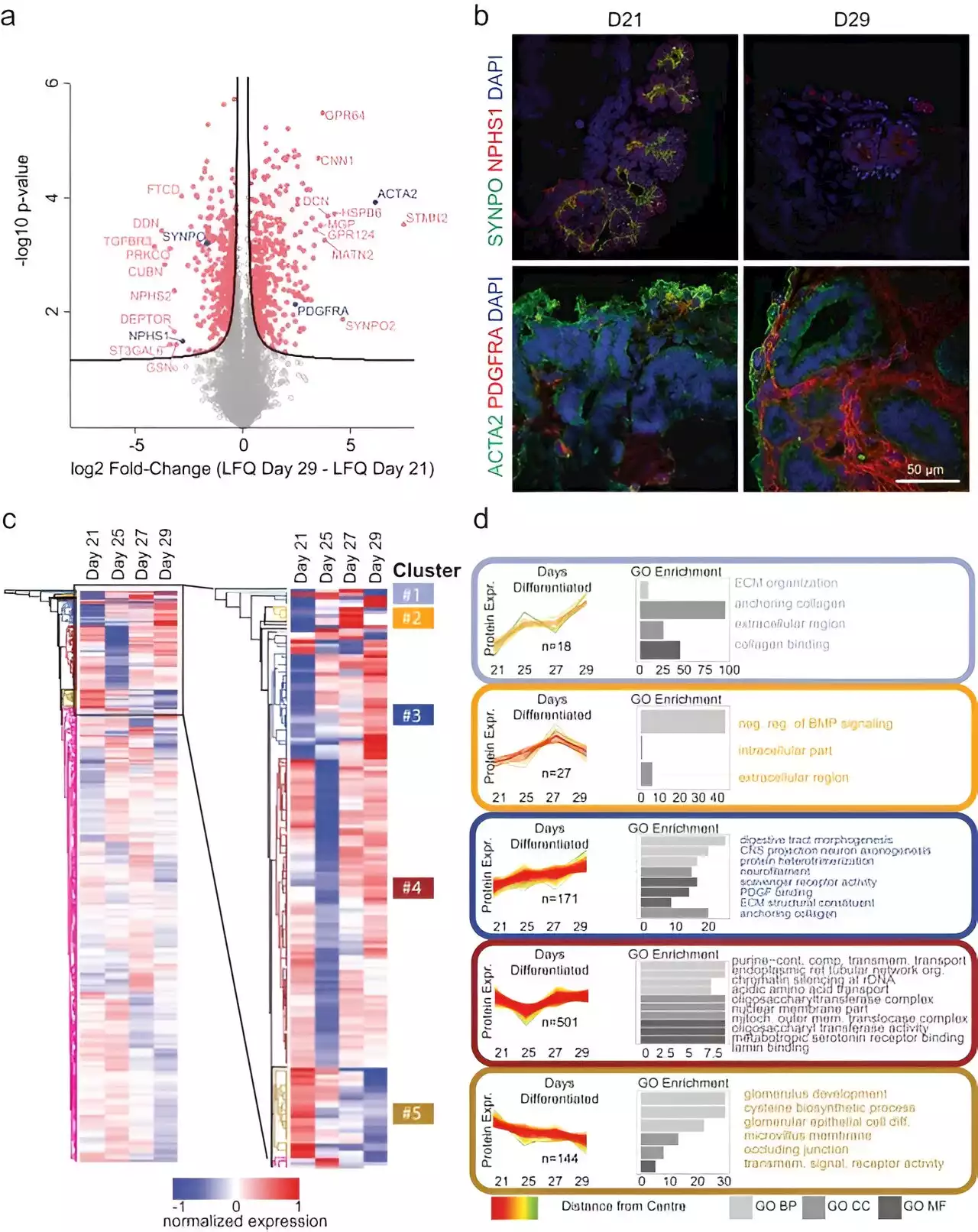
to confirm the patterns of increased extracellular matrix protein production with increased duration of cell culture.
Organoid proteome organization shows similarities with human kidneys. a Venn diagram of the organoid proteome compared with microdissected single glomeruli and tubules proteomes. Four compartments indicate proteins identified in single glomeruli only, both single glomeruli and organoids, single tubules only, and both single tubules and organoids.