Does air pollution reduce cognitive function over time? AirPollution CognitiveFunction Pollution Cognition MetaAnalysis imperialcollege STOTEN_journal
By Dr. Liji Thomas, MDDec 4 2022Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. In a recent Science of the Total Environment study, researchers in the United Kingdom examine available studies for significant correlations between declining cognitive function in childhood and adult life and air pollution parameters. The study findings provide evidence of the inextricable interweaving of networks linking human environmental and individual health to productivity and socioeconomic background.
Cognition refers to mental processes involved in learning and using knowledge or information. This includes acquiring, processing, transforming, and storing such data with timely retrieval. Good cognitive skills are key to maintaining good physical and mental health, achieving academic success, rising in society, and earning more.
Most studies in the meta-analysis explored air quality at home or school, thus measuring potential exposure to air pollution in the form of particulate matter less than or equal to 2.5 micrometers in size . For children and adolescents, the risk of exposure-linked general cognitive deterioration was not supported by research; however, the strength of the evidence is too weak to make a definitive conclusion.
Available research does not support an association between memory and learning or between reaction time and the speed at which a child processes data or exposure to various air pollutants like NOx, PM2.5, and ultrafine particles .In those above the age of 40, some associations with general cognitive decline and PM2.5 or NOx exposure were identified. In addition, PM2.5 exposure was also associated with reduced verbal fluency and executive function.
Despite the limited number of studies on young adults, this group appears to be more affected by exposure to air pollution than children or older adults. Further research is thus essential in this group, as the brain rapidly develops up to the age of 25 years and continues after that at a slower pace until the end of life.
Such differences in the latent period before injury become apparent following an acute injury or with different pollutants. This phenomenon was evident in one study where short-term effects on general cognitive function were more significantly associated with PM2.5 than with NOx. However, the converse effects were seen with long-term consequences for these two pollutant types.
Danmark Seneste Nyt, Danmark Overskrifter
Similar News:Du kan også læse nyheder, der ligner denne, som vi har indsamlet fra andre nyhedskilder.
 Osaska University Scientists Work Towards Eliminating Key Bottlenecks In Hydrogen | OilPrice.comOsaka University researchers have demonstrated a proof-of-concept for a novel molecular hydrogen production method that bypasses the need for expensive purification steps
Osaska University Scientists Work Towards Eliminating Key Bottlenecks In Hydrogen | OilPrice.comOsaka University researchers have demonstrated a proof-of-concept for a novel molecular hydrogen production method that bypasses the need for expensive purification steps
Læs mere »
 Trial shows acoziborole drug clears body of African sleeping sickness parasitesTrial shows acoziborole drug clears body of African sleeping sickness parasites Efficacy African SleepingSickness Antimicrobial Drug ClinicalTrial Trypanosomiasis TheLancetInfDis
Trial shows acoziborole drug clears body of African sleeping sickness parasitesTrial shows acoziborole drug clears body of African sleeping sickness parasites Efficacy African SleepingSickness Antimicrobial Drug ClinicalTrial Trypanosomiasis TheLancetInfDis
Læs mere »
 Perfect winter walk ending with a well earned pint at a cosy pubPerfect Lancashire winter walk that ends with a well earned pint at a cosy pub
Perfect winter walk ending with a well earned pint at a cosy pubPerfect Lancashire winter walk that ends with a well earned pint at a cosy pub
Læs mere »
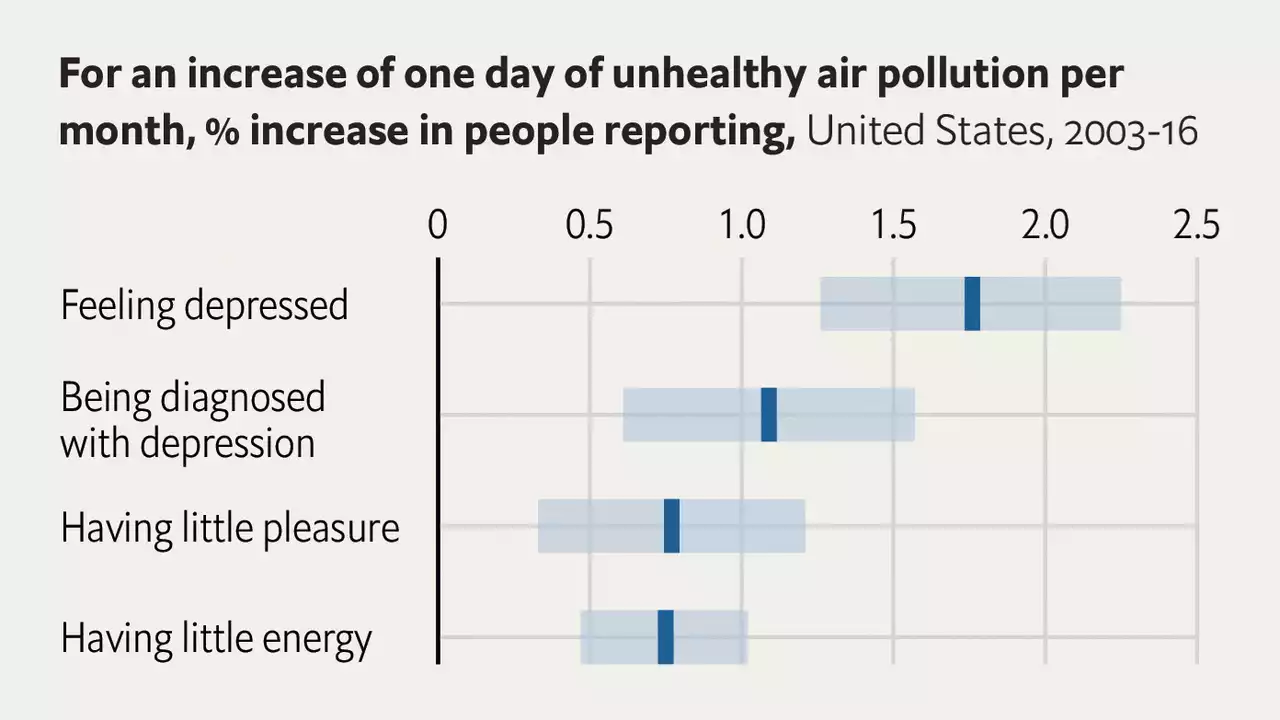 Air pollution can drive people to kill themselvesThere are geographical variations. Researchers found that the impact of pollution on suicide rates was greatest in poorer counties and in those with more unemployment
Air pollution can drive people to kill themselvesThere are geographical variations. Researchers found that the impact of pollution on suicide rates was greatest in poorer counties and in those with more unemployment
Læs mere »
 Missed Strictly Due To The Schedule Change? Here's Everything That Happened During Musicals WeekThe show aired a day earlier than usual due to the BBC's World Cup coverage.
Missed Strictly Due To The Schedule Change? Here's Everything That Happened During Musicals WeekThe show aired a day earlier than usual due to the BBC's World Cup coverage.
Læs mere »
 Top Of The Pops Christmas special 'axed' by BBC after 57 yearsThe BBC has reportedly canceled the Top Of The Pops Christmas special after gracing our screens for nearly six decades.
Top Of The Pops Christmas special 'axed' by BBC after 57 yearsThe BBC has reportedly canceled the Top Of The Pops Christmas special after gracing our screens for nearly six decades.
Læs mere »
